Complete genome phasing of family quartet by combination of genetic, physical and population-based phasing analysis
- PMID: 23741343
- PMCID: PMC3669306
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064571
Complete genome phasing of family quartet by combination of genetic, physical and population-based phasing analysis
Abstract
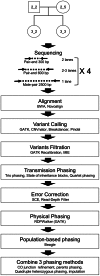
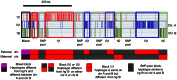
Phased genome maps are important to understand genetic and epigenetic regulation and disease mechanisms, particularly parental imprinting defects. Phasing is also critical to assess the functional consequences of genetic variants, and to allow precise definition of haplotype blocks which is useful to understand gene-flow and genotype-phenotype association at the population level. Transmission phasing by analysis of a family quartet allows the phasing of 95% of all variants as the uniformly heterozygous positions cannot be phased. Here, we report a phasing method based on a combination of transmission analysis, physical phasing by pair-end sequencing of libraries of staggered sizes and population-based analysis. Sequencing of a healthy Caucasians quartet at 120x coverage and combination of physical and transmission phasing yielded the phased genotypes of about 99.8% of the SNPs, indels and structural variants present in the quartet, a phasing rate significantly higher than what can be achieved using any single phasing method. A false positive SNP error rate below 10*E-7 per genome and per base was obtained using a combination of filters. We provide a complete list of SNPs, indels and structural variants, an analysis of haplotype block sizes, and an analysis of the false positive and negative variant calling error rates. Improved genome phasing and family sequencing will increase the power of genome-wide sequencing as a clinical diagnosis tool and has myriad basic science applications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
trioPhaser: using Mendelian inheritance logic to improve genomic phasing of trios.BMC Bioinformatics. 2021 Nov 22;22(1):559. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04470-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 34809557 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid peeling for fast and accurate calling, phasing, and imputation with sequence data of any coverage in pedigrees.Genet Sel Evol. 2018 Dec 18;50(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12711-018-0438-2. Genet Sel Evol. 2018. PMID: 30563452 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of phasing strategies for whole human genomes.PLoS Genet. 2018 Apr 5;14(4):e1007308. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007308. eCollection 2018 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 29621242 Free PMC article.
-
Towards accurate, contiguous and complete alignment-based polyploid phasing algorithms.Genomics. 2022 May;114(3):110369. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2022.110369. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35483655 Review.
-
Haplotyping-Assisted Diploid Assembly and Variant Detection with Linked Reads.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2590:161-182. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2819-5_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36335499 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic analyses provide insights into breed-of-origin effects from purebreds on three-way crossbred pigs.PeerJ. 2019 Nov 11;7:e8009. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8009. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31737448 Free PMC article.
-
Allele-specific analysis of DNA replication origins in mammalian cells.Nat Commun. 2015 May 19;6:7051. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8051. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25987481 Free PMC article.
-
Allele-specific genome-wide profiling in human primary erythroblasts reveal replication program organization.PLoS Genet. 2014 May 1;10(5):e1004319. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004319. eCollection 2014 May. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 24787348 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome haplotyping approaches and genomic medicine.Genome Med. 2014 Sep 25;6(9):73. doi: 10.1186/s13073-014-0073-7. eCollection 2014. Genome Med. 2014. PMID: 25473435 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of establishment and functional significance of DNA demethylation during erythroid differentiation.Blood Adv. 2018 Aug 14;2(15):1833-1852. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018015651. Blood Adv. 2018. PMID: 30061308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li HH, Gyllensten UB, Cui XF, Saiki RK, Erlich HA, et al. (1988) Amplification and analysis of DNA sequences in single human sperm and diploid cells. Nature 335: 414–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

