Prospective ECG-triggered coronary CT angiography: clinical value of noise-based tube current reduction method with iterative reconstruction
- PMID: 23741444
- PMCID: PMC3669389
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065025
Prospective ECG-triggered coronary CT angiography: clinical value of noise-based tube current reduction method with iterative reconstruction
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the clinical value of noise-based tube current reduction method with iterative reconstruction for obtaining consistent image quality with dose optimization in prospective electrocardiogram (ECG)-triggered coronary CT angiography (CCTA).
Materials and methods: We performed a prospective randomized study evaluating 338 patients undergoing CCTA with prospective ECG-triggering. Patients were randomly assigned to fixed tube current with filtered back projection (Group 1, n = 113), noise-based tube current with filtered back projection (Group 2, n = 109) or with iterative reconstruction (Group 3, n = 116). Tube voltage was fixed at 120 kV. Qualitative image quality was rated on a 5-point scale (1 = impaired, to 5 = excellent, with 3-5 defined as diagnostic). Image noise and signal intensity were measured; signal-to-noise ratio was calculated; radiation dose parameters were recorded. Statistical analyses included one-way analysis of variance, chi-square test, Kruskal-Wallis test and multivariable linear regression.
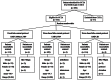
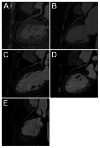
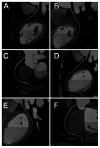
Results: Image noise was maintained at the target value of 35HU with small interquartile range for Group 2 (35.00-35.03HU) and Group 3 (34.99-35.02HU), while from 28.73 to 37.87HU for Group 1. All images in the three groups were acceptable for diagnosis. A relative 20% and 51% reduction in effective dose for Group 2 (2.9 mSv) and Group 3 (1.8 mSv) were achieved compared with Group 1 (3.7 mSv). After adjustment for scan characteristics, iterative reconstruction was associated with 26% reduction in effective dose.
Conclusion: Noise-based tube current reduction method with iterative reconstruction maintains image noise precisely at the desired level and achieves consistent image quality. Meanwhile, effective dose can be reduced by more than 50%.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Noise-based tube current reduction method with iterative reconstruction for reduction of radiation exposure in coronary CT angiography.Eur J Radiol. 2013 Feb;82(2):349-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2012.10.008. Epub 2012 Nov 7. Eur J Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23140592
-
The feasibility of sub-millisievert coronary CT angiography with low tube voltage, prospective ECG gating, and a knowledge-based iterative model reconstruction algorithm.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015 Dec;31 Suppl 2:197-203. doi: 10.1007/s10554-015-0795-7. Epub 2015 Oct 31. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26521066
-
Effect of reduced x-ray tube voltage, low iodine concentration contrast medium, and sinogram-affirmed iterative reconstruction on image quality and radiation dose at coronary CT angiography: results of the prospective multicenter REALISE trial.J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2015 May-Jun;9(3):215-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2015.01.010. Epub 2015 Jan 22. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 2015. PMID: 25843243 Clinical Trial.
-
Non-inferior low-dose coronary computed tomography angiography image quality with knowledge-based iterative model reconstruction for overweight patients.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 26;13(12):e0209243. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209243. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30586449 Free PMC article.
-
The optimal dose reduction level using iterative reconstruction with prospective ECG-triggered coronary CTA using 256-slice MDCT.Eur J Radiol. 2012 Dec;81(12):3905-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2012.06.022. Epub 2012 Oct 1. Eur J Radiol. 2012. PMID: 23036786
Cited by
-
Safety and efficacy of intravenous esmolol before prospective electrocardiogram-triggered high-pitch spiral acquisition for computed tomography coronary angiography.J Geriatr Cardiol. 2014 Mar;11(1):39-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5411.2014.01.011. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24748880 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation dose reduction for CT assessment of urolithiasis using iterative reconstruction: A prospective intra-individual study.Eur Radiol. 2018 Jan;28(1):143-150. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-4929-2. Epub 2017 Jul 10. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 28695359 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic tube potential selection with tube current modulation in coronary CT angiography: Can it achieve consistent image quality among various individuals?Exp Ther Med. 2018 Jul;16(1):253-259. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6158. Epub 2018 May 11. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29896246 Free PMC article.
-
Image Quality and Radiation Dose of CT Coronary Angiography with Automatic Tube Current Modulation and Strong Adaptive Iterative Dose Reduction Three-Dimensional (AIDR3D).PLoS One. 2015 Nov 23;10(11):e0142185. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142185. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26599111 Free PMC article.
-
Image noise-based dose adaptation in dynamic volume CT of the heart: dose and image quality optimisation in comparison with BMI-based dose adaptation.Eur Radiol. 2014 Jan;24(1):86-94. doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-2980-1. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Eur Radiol. 2014. PMID: 23949725
References
-
- Miller JM, Rochitte CE, Dewey M, Arbab-Zadeh A, Niinuma H, et al. (2008) Diagnostic performance of coronary angiography by 64-row CT. N Engl J Med 359: 2324–2336. - PubMed
-
- Hausleiter J, Meyer T, Hadamitzky M, Huber E, Zankl M, et al. (2006) Radiation dose estimates from cardiac multislice computed tomography in daily practice: impact of different scanning protocols on effective dose estimates. Circulation 113: 1305–1310. - PubMed
-
- Einstein AJ, Henzlova MJ, Rajagopalan S (2007) Estimating risk of cancer associated with radiation exposure from 64-slice computed tomography coronary angiography. JAMA 298: 317–323. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh J, Londt J, Vass M, Li J, Tang X, et al. (2006) Step-and-shoot data acquisition and reconstruction for cardiac x-ray computed tomography. Med Phys 33: 4236–4248. - PubMed
-
- Sun Z, Ng KH (2012) Prospective versus retrospective ECG-gated multislice CT coronary angiography: a systematic review of radiation dose and diagnostic accuracy. Eur J Radiol 81: e94–e100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

