Non-apoptotic function of caspases in a cellular model of hydrogen peroxide-associated colitis
- PMID: 23742011
- PMCID: PMC3822895
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12079
Non-apoptotic function of caspases in a cellular model of hydrogen peroxide-associated colitis
Abstract
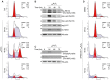
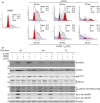
Oxidative stress, caused by reactive oxygen species (ROS), is a major contributor to inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)-associated neoplasia. We mimicked ROS exposure of the epithelium in IBD using non-tumour human colonic epithelial cells (HCEC) and hydrogen peroxide (H2 O2 ). A population of HCEC survived H2 O2 -induced oxidative stress via JNK-dependent cell cycle arrests. Caspases, p21(WAF1) and γ-H2AX were identified as JNK-regulated proteins. Up-regulation of caspases was linked to cell survival and not, as expected, to apoptosis. Inhibition using the pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK caused up-regulation of γ-H2AX, a DNA-damage sensor, indicating its negative regulation via caspases. Cell cycle analysis revealed an accumulation of HCEC in the G1 -phase as first response to oxidative stress and increased S-phase population and then apoptosis as second response following caspase inhibition. Thus, caspases execute a non-apoptotic function by promoting cells through G1 - and S-phase by overriding the G1 /S- and intra-S checkpoints despite DNA-damage. This led to the accumulation of cells in the G2 /M-phase and decreased apoptosis. Caspases mediate survival of oxidatively damaged HCEC via γ-H2AX suppression, although its direct proteolytic inactivation was excluded. Conversely, we found that oxidative stress led to caspase-dependent proteolytic degradation of the DNA-damage checkpoint protein ATM that is upstream of γ-H2AX. As a consequence, undetected DNA-damage and increased proliferation were found in repeatedly H2 O2 -exposed HCEC. Such features have been associated with neoplastic transformation and appear here to be mediated by a non-apoptotic function of caspases. Overexpression of upstream p-JNK in active ulcerative colitis also suggests a potential importance of this pathway in vivo.
Keywords: ATM degradation; DNA-damage checkpoints; JNK-dependent cell cycle arrests; hydrogen peroxide-associated colitis; inflammation; neoplastic transformation; non-apoptotic caspase function; γ-H2AX.
© 2013 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine Published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Repeated H2 O2 exposure drives cell cycle progression in an in vitro model of ulcerative colitis.J Cell Mol Med. 2013 Dec;17(12):1619-31. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12150. Epub 2013 Oct 9. J Cell Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 24118792 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen peroxide and Helicobacter pylori extract treatment combined with APE1 knockdown induce DNA damage, G2/M arrest and cell death in gastric cancer cell line.DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 Dec;96:102976. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102976. Epub 2020 Sep 28. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 33065487
-
Ovatodiolide isolated from Anisomeles indica induces cell cycle G2/M arrest and apoptosis via a ROS-dependent ATM/ATR signaling pathways.Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Jan 15;819:16-29. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.09.050. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28986085
-
Lethal and Non-Lethal Functions of Caspases in the DNA Damage Response.Cells. 2022 Jun 10;11(12):1887. doi: 10.3390/cells11121887. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35741016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How does caspases regulation play role in cell decisions? apoptosis and beyond.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Jul;479(7):1599-1613. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04870-5. Epub 2023 Nov 17. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37976000 Review.
Cited by
-
Downregulation of lncRNA CCAT1 enhances 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in human colon cancer cells.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Apr 23;20(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12860-019-0188-1. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31039730 Free PMC article.
-
Chk1 Promotes DNA Damage Response Bypass following Oxidative Stress in a Model of Hydrogen Peroxide-Associated Ulcerative Colitis through JNK Inactivation and Chromatin Binding.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:9303158. doi: 10.1155/2017/9303158. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28751935 Free PMC article.
-
Selenium-Containing Amino Acids Protect Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis via Ameliorating Oxidative Stress and Intestinal Inflammation.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Jan 14;14:85-95. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S288412. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 33488110 Free PMC article.
-
Role of miR-223-3p in pulmonary arterial hypertension via targeting ITGB3 in the ECM pathway.Cell Prolif. 2019 Mar;52(2):e12550. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12550. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Cell Prolif. 2019. PMID: 30507047 Free PMC article.
-
Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Bisphenol A Interact with Doxorubicin Transcriptional Effects in Human Cell Lines.Toxics. 2019 Aug 29;7(3):43. doi: 10.3390/toxics7030043. Toxics. 2019. PMID: 31470548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Colotta F, Allavena P, Sica A, et al. Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark of cancer: links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:1073–81. - PubMed
-
- Kundu JK, Surh YJ. Inflammation: gearing the journey to cancer. Mutat Res. 2008;659:15–30. - PubMed
-
- Roessner A, Kuester D, Malfertheiner P, et al. Oxidative stress in ulcerative colitis-associated carcinogenesis. Pathol Res Pract. 2008;204:511–24. - PubMed
-
- Terzic J, Grivennikov S, Karin E, et al. Inflammation and colon cancer. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:2101–14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

