Crosstalk between hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide in endothelial cells
- PMID: 23742697
- PMCID: PMC3822893
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12077
Crosstalk between hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide in endothelial cells
Abstract
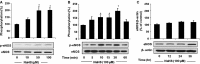
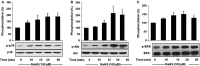
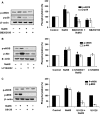
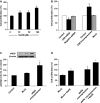
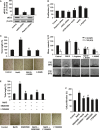
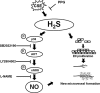
Hydrogen sulfide (H2 S) and nitric oxide (NO) are major gasotransmitters produced in endothelial cells (ECs), contributing to the regulation of vascular contractility and structural integrity. Their interaction at different levels would have a profound impact on angiogenesis. Here, we showed that H2 S and NO stimulated the formation of new microvessels. Incubation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs-926) with NaHS (a H2 S donor) stimulated the phosphorylation of endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) and enhanced NO production. H2 S had little effect on eNOS protein expression in ECs. L-cysteine, a precursor of H2 S, stimulated NO production whereas blockage of the activity of H2 S-generating enzyme, cystathionine gamma-lyase (CSE), inhibited this action. CSE knockdown inhibited, but CSE overexpression increased, NO production as well as EC proliferation. LY294002 (Akt/PI3-K inhibitor) or SB203580 (p38 MAPK inhibitor) abolished the effects of H2 S on eNOS phosphorylation, NO production, cell proliferation and tube formation. Blockade of NO production by eNOS-specific siRNA or nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) reversed, but eNOS overexpression potentiated, the proliferative effect of H2 S on ECs. Our results suggest that H2 S stimulates the phosphorylation of eNOS through a p38 MAPK and Akt-dependent pathway, thus increasing NO production in ECs and vascular tissues and contributing to H2 S-induced angiogenesis.
Keywords: CSE; Cystathionine gamma-lyase; Endothelial cells; Hydrogen sulfide; Nitric oxide; eNOS.
© 2013 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine Published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine/Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Wang R. Two's company, three's a crowd – Can H2S be the third endogenous gaseous transmitter? FASEB J. 2002;13:1792–8. - PubMed
-
- Murad F. Cellular signaling with nitric oxide and cyclic GMP. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1999;32:1317–27. - PubMed
-
- Klatt P, Schmidt K, Uray G, et al. Multiple catalytic functions of brain nitric oxide synthase. Biochemical characterization, cofactor-requirement, and the role of N omega-hydroxy-L-arginine as an intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:14781–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

