The arrival of JAK inhibitors: advancing the treatment of immune and hematologic disorders
- PMID: 23743669
- PMCID: PMC3778139
- DOI: 10.1007/s40259-013-0040-7
The arrival of JAK inhibitors: advancing the treatment of immune and hematologic disorders
Abstract
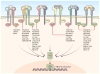
Altered production of cytokines can result in pathologies ranging from autoimmune diseases to malignancies. The Janus kinase family is a small group of receptor-associated signaling molecules that is essential to the signal cascade originating from type I and type II cytokine receptors. Inhibition of tyrosine kinase enzymatic activity using small molecules has recently become a powerful tool for treatment of several malignancies. Twenty years after the discovery of these enzymes, two inhibitors for this class of kinases have been approved for clinical use and others are currently in the final stage of development. Here we review the principles of cytokines signaling, summarize our current knowledge of the approved inhibitors, and briefly introduce some of the inhibitors that are currently under development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
JAK/STAT Signal Transduction: Promising Attractive Targets for Immune, Inflammatory and Hematopoietic Diseases.Curr Drug Targets. 2018;19(5):487-500. doi: 10.2174/1389450117666161207163054. Curr Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 27928945 Review.
-
Janus kinases: an ideal target for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2013 Dec;16(1):S70-2. doi: 10.1038/jidsymp.2013.29. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2013. PMID: 24326567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of JAK inhibitors for the treatment of immune-mediated diseases: kinase-targeted inhibitors and pseudokinase-targeted inhibitors.Arch Pharm Res. 2020 Nov;43(11):1173-1186. doi: 10.1007/s12272-020-01282-7. Epub 2020 Nov 8. Arch Pharm Res. 2020. PMID: 33161563 Review.
-
The role of JAK/STAT signaling pathway and its inhibitors in diseases.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Mar;80:106210. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106210. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31972425 Review.
-
Emerging therapeutic paradigms to target the dysregulated Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway in hematological malignancies.Leuk Lymphoma. 2014 Sep;55(9):1968-79. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2013.863307. Epub 2014 Feb 17. Leuk Lymphoma. 2014. PMID: 24206094 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Restoring the balance: immunotherapeutic combinations for autoimmune disease.Dis Model Mech. 2014 May;7(5):503-13. doi: 10.1242/dmm.015099. Dis Model Mech. 2014. PMID: 24795433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tofacitinib use in ulcerative colitis: An expert consensus for day-to-day clinical practice.Indian J Gastroenterol. 2024 Feb;43(1):22-35. doi: 10.1007/s12664-023-01507-9. Epub 2024 Feb 12. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38347433
-
Identification of Prognostic Biomarkers and Molecular Targets Among JAK Family in Breast Cancer.J Inflamm Res. 2021 Jan 14;14:97-114. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S284889. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 33469338 Free PMC article.
-
Norovirus Replication in Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells Is Restricted by the Interferon-Induced JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway and RNA Polymerase II-Mediated Transcriptional Responses.mBio. 2020 Mar 17;11(2):e00215-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00215-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32184238 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating tofacitinib citrate in the treatment of moderate-to-severe active ulcerative colitis: design, development and positioning of therapy.Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2019 May 2;12:179-191. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S150908. eCollection 2019. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31118734 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leonard WJ, O’Shea JJ. Jaks and STATs: biological implications. Annual review of immunology. 1998;16:293–322. Epub 1998/05/23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

