Life's Simple 7 and risk of incident stroke: the reasons for geographic and racial differences in stroke study
- PMID: 23743971
- PMCID: PMC3816734
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.000352
Life's Simple 7 and risk of incident stroke: the reasons for geographic and racial differences in stroke study
Abstract
Background and purpose: The American Heart Association developed Life's Simple 7 (LS7) as a metric defining cardiovascular health. We investigated the association between LS7 and incident stroke in black and white Americans.
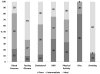
Methods: The Reasons for Geographic And Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) is a national population-based cohort of 30 239 blacks and whites, aged ≥45 years, sampled from the US population from 2003 to 2007. Data were collected by telephone, self-administered questionnaires, and an in-home examination. Incident strokes were identified through biannual participant contact followed by adjudication of medical records. Levels of the LS7 components (blood pressure, cholesterol, glucose, body mass index, smoking, physical activity, and diet) were each coded as poor (0 point), intermediate (1 point), or ideal (2 points) health. An overall LS7 score was categorized as inadequate (0-4), average (5-9), or optimum (10-14) cardiovascular health.
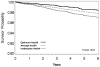
Results: Among 22 914 subjects with LS7 data and no previous cardiovascular disease, there were 432 incident strokes over 4.9 years of follow-up. After adjusting for demographics, socioeconomic status, and region of residence, each better health category of the LS7 score was associated with a 25% lower risk of stroke (hazard ratios, 0.75; 95% confidence interval, 0.63-0.90). The association was similar for blacks and whites (interaction P value=0.55). A 1-point higher LS7 score was associated with an 8% lower risk of stroke (hazard ratios, 0.92; 95% confidence interval, 0.88-0.95).
Conclusions: In both blacks and whites, better cardiovascular health, on the basis of the LS7 score, is associated with lower risk of stroke, and a small difference in scores was an important stroke determinant.
Keywords: racial differences; risk factors; stroke.
Figures
References
-
- Heidenreich PA, Trogdon JG, Khavjou OA, Butler J, Dracup K, Ezekowitz MD, et al. Forecasting the future of cardiovascular disease in the United States: a policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011;123:933–44. - PubMed
-
- Stamler J, Stamler R, Neaton JD, Wentworth D, Daviglus ML, Garside D, et al. Low risk-factor profile and long-term cardiovascular and noncardiovascular mortality and life expectancy: findings for 5 large cohorts of young adult and middle-aged men and women. JAMA. 1999;282:2012–8. - PubMed
-
- Vasan RS, Sullivan LM, Wilson PW, Sempos CT, Sundstrom J, Kannel WB, et al. Relative importance of borderline and elevated levels of coronary heart disease risk factors. Ann Intern Med. 2005;142:393–402. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd-Jones DM, Hong Y, Labarthe D, Mozaffarian D, Appel LJ, Van Horn L, et al. Defining and setting national goals for cardiovascular health promotion and disease reduction: the American Heart Association’s strategic Impact Goal through 2020 and beyond. Circulation. 2010;121:586–613. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein LB, Bushnell CD, Adams RJ, Appel LJ, Braun LT, Chaturvedi S, et al. Guidelines for the primary prevention of stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2011;42:517–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical