Immunomodulators and immunosuppressants for multiple sclerosis: a network meta-analysis
- PMID: 23744561
- PMCID: PMC11627144
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008933.pub2
Immunomodulators and immunosuppressants for multiple sclerosis: a network meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Different therapeutic strategies are available for treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS) including immunosuppressants, immunomodulators, and monoclonal antibodies. Their relative effectiveness in the prevention of relapse or disability progression is unclear due to the limited number of direct comparison trials. A summary of the results, including both direct and indirect comparisons of treatment effects, may help to clarify the above uncertainty.
Objectives: To estimate the relative efficacy and acceptability of interferon ß-1b (IFNß-1b) (Betaseron), interferon ß-1a (IFNß-1a) (Rebif and Avonex), glatiramer acetate, natalizumab, mitoxantrone, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, azathioprine, intravenous immunoglobulins, and long-term corticosteroids versus placebo or another active agent in participants with MS and to provide a ranking of the treatments according to their effectiveness and risk-benefit balance.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, the Cochrane MS Group Trials Register, and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reports. The most recent search was run in February 2012.
Selection criteria: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that studied one of the 11 treatments for use in adults with MS and that reported our pre-specified efficacy outcomes were considered for inclusion.
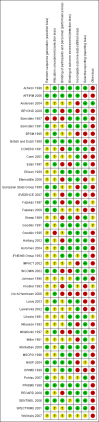
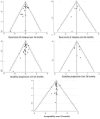
Data collection and analysis: Identifying search results and data extraction were performed independently by two authors. Data synthesis was performed by pairwise meta-analysis and network meta-analysis that was performed within a Bayesian framework. The body of evidence for outcomes within the pairwise meta-analysis was assessed according to GRADE, as very low, low, moderate, or high quality.
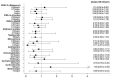
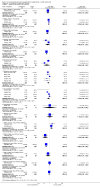
Main results: Forty-four trials were included in this review, in which 17,401 participants had been randomised. Twenty-three trials included relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) (9096 participants, 52%), 18 trials included progressive MS (7726, 44%), and three trials included both RRMS and progressive MS (579, 3%). The majority of the included trials were short-term studies, with the median duration being 24 months. The results originated mostly from 33 trials on IFNß, glatiramer acetate, and natalizumab that overall contributed outcome data for 9881 participants (66%).From the pairwise meta-analysis, there was high quality evidence that natalizumab and IFNß-1a (Rebif) were effective against recurrence of relapses in RRMS during the first 24 months of treatment compared to placebo (odds ratio (OR) 0.32, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.24 to 0.43; OR 0.45, 95% CI 0.28 to 0.71, respectively); they were more effective than IFNß-1a (Avonex) (OR 0.28, 95% CI 0.22 to 0.36; OR 0.19, 95% CI 0.06 to 0.60, respectively). IFNß-1b (Betaseron) and mitoxantrone probably decreased the odds of the participants with RRMS having clinical relapses compared to placebo (OR 0.55, 95% CI 0.31 to 0.99; OR 0.15, 95% CI 0.04 to 0.54, respectively) but the quality of evidence for these treatments was graded as moderate. From the network meta-analysis, the most effective drug appeared to be natalizumab (median OR versus placebo 0.29, 95% credible intervals (CrI) 0.17 to 0.51), followed by IFNß-1a (Rebif) (median OR versus placebo 0.44, 95% CrI 0.24 to 0.70), mitoxantrone (median OR versus placebo 0.43, 95% CrI 0.20 to 0.87), glatiramer acetate (median OR versus placebo 0.48, 95% CrI 0.38 to 0.75), IFNß-1b (Betaseron) (median OR versus placebo 0.48, 95% CrI 0.29 to 0.78). However, our confidence was moderate for direct comparison of mitoxantrone and IFNB-1b vs placebo and very low for direct comparison of glatiramer vs placebo. The relapse outcome for RRMS at three years' follow-up was not reported by any of the included trials.Disability progression was based on surrogate markers in the majority of included studies and was unavailable for RRMS beyond two to three years. The pairwise meta-analysis suggested, with moderate quality evidence, that natalizumab and IFNß-1a (Rebif) probably decreased the odds of the participants with RRMS having disability progression at two years' follow-up, with an absolute reduction of 14% and 10%, respectively, compared to placebo. Natalizumab and IFNß-1b (Betaseron) were significantly more effective (OR 0.62, 95% CI 0.49 to 0.78; OR 0.35, 95% CI 0.17 to 0.70, respectively) than IFNß-1a (Avonex) in reducing the number of the participants with RRMS who had progression at two years' follow-up, and confidence in this result was graded as moderate. From the network meta-analyses, mitoxantrone appeared to be the most effective agent in decreasing the odds of the participants with RRMS having progression at two years' follow-up, but our confidence was very low for direct comparison of mitoxantrone vs placebo. Both pairwise and network meta-analysis revealed that none of the individual agents included in this review were effective in preventing disability progression over two or three years in patients with progressive MS.There was not a dose-effect relationship for any of the included treatments with the exception of mitoxantrone.
Authors' conclusions: Our review should provide some guidance to clinicians and patients. On the basis of high quality evidence, natalizumab and IFNß-1a (Rebif) are superior to all other treatments for preventing clinical relapses in RRMS in the short-term (24 months) compared to placebo. Moderate quality evidence supports a protective effect of natalizumab and IFNß-1a (Rebif) against disability progression in RRMS in the short-term compared to placebo. These treatments are associated with long-term serious adverse events and their benefit-risk balance might be unfavourable. IFNß-1b (Betaseron) and mitoxantrone probably decreased the odds of the participants with RRMS having relapses, compared with placebo (moderate quality of evidence). The benefit-risk balance with azathioprine is uncertain, however this agent might be effective in decreasing the odds of the participants with RRMS having relapses and disability progression over 24 to 36 months, compared with placebo. The lack of convincing efficacy data shows that IFNß-1a (Avonex), intravenous immunoglobulins, cyclophosphamide and long-term steroids have an unfavourable benefit-risk balance in RRMS. None of the included treatments are effective in decreasing disability progression in patients with progressive MS. It is important to consider that the clinical effects of all these treatments beyond two years are uncertain, a relevant point for a disease of 30 to 40 years duration. Direct head-to-head comparison(s) between natalizumab and IFNß-1a (Rebif) or between azathioprine and IFNß-1a (Rebif) should be top priority on the research agenda and follow-up of the trial cohorts should be mandatory.
Conflict of interest statement
GF ‐ none
GS ‐ none
CDG ‐ none
DB ‐ none
LV ‐ none
RDA ‐ none
CDP ‐ None
Figures











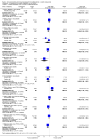
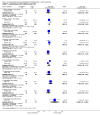



Comment in
-
Intramuscular IFNß-1a in multiple sclerosis: 'no proof of effectiveness' or 'proof of no effectiveness'?Eur J Neurol. 2013 Dec;20(12):e131. doi: 10.1111/ene.12275. Eur J Neurol. 2013. PMID: 24433477 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Achiron 1998 {published data only}
-
- Achiron A, Gabbay U, Gilad R, Hassin B, Barak Y, Gornish M, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in multiple sclerosis. Effect on relapses. Neurology 1998;50(2):398‐402. - PubMed
AFFIRM 2006 {published data only}
-
- Polman CH, O'Connor PW, Havrdova E, Hutchinson M, Kappos L, Miller DH, et al. A randomized, placebo‐controlled trial of natalizumab for relapsing multiple sclerosis. The New England Journal of Medicine 2006;354(9):899‐910. - PubMed
Andersen 2004 {published data only}
-
- Andersen O, Elovaara I, Farkkila M, Hansen HJ, Mellgren SI, Myhr KM, et al. Multicentre, randomised, double blind, placebo controlled, phase III study of weekly, low dose, subcutaneous interferon beta‐1a in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 2004;75(5):706‐10. [PUBMED: 15090564] - PMC - PubMed
BEYOND 2009 {published data only}
-
- O'Connor P, Filippi M, Arnason B, Comi G, Cook S, Goodin D, et al. 250 microg or 500 microg interferon beta‐1b versus 20 mg glatiramer acetate in relapsing‐remitting multiple sclerosis: a prospective, randomised, multicentre study. Lancet Neurology 2009;8(10):889‐97. - PubMed
Bornstein 1987 {published data only}
-
- Bornstein MB, Miller A, Slagle, S, Weitzman M, Crystal, et al. A pilot trial of Cop 1 in exacerbating‐remitting multiple sclerosis. The New England Journal of Medicine 1987; Vol. 317, issue 7:408‐14. - PubMed
Bornstein 1991 {published data only}
-
- Bornstein MB, Miller A, Slagle S, Weitzman M, Drexler E, Keilson Metal. A placebo‐controlled, double‐blind, randomised, two‐center, pilot trial of Cop 1 in chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. Neurology 1991;41:533‐9. [DOI] - PubMed
BPSM 1995 {published data only}
British and Dutch 1988 {published data only}
-
- The British, Dutch MSATG. Double‐masked trial of azathioprine in multiple sclerosis. Lancet 1988; Vol. 2, issue 8604:179‐83. - PubMed
CCMSSG 1991 {published data only}
-
- CCMSSG. The Canadian cooperative trial of cyclophosphamide and plasma exchange in progressive multiple sclerosis. Lancet 1991;337(8739):441‐6. - PubMed
Comi 2001 {published data only}
-
- Comi G, Filippi M, Wolinsky JS. European/Canadian multicenter, double‐blind, randomized, placebo‐controlled study of the effects of glatiramer acetate on magnetic resonance imaging‐‐measured disease activity and burden in patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis. European/Canadian Glatiramer Acetate Study Group. Annals of Neurology 2001;49(3):290‐7. [PUBMED: 11261502] - PubMed
Edan 1997 {published data only}
-
- Edan G, Miller D, Clanet M, Confavreux C, Lyon‐Caen O, Lubetzki C, et al. Therapeutic effect of mitoxantrone combined with methylprednisolone in multiple sclerosis: a randomised multicentre study of active disease using MRI and clinical criteria. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1997;62(2):112‐8. [DOI] - PMC - PubMed
Ellison 1989 {published data only}
-
- Ellison G, Myers L, Mickey M, Graves M, Tourtellotte W, Syndulko K, et al. A placebo‐controlled, randomized, double‐masked, variable dosage, clinical trial of azathioprine with and without methylprednisolone in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 1989;39(8):1018‐26. - PubMed
Etemadifar 2006 {published data only}
-
- Etemadifar M, Janghorbani M, Shaygannejad V. Comparison of Betaferon, Avonex, and Rebif in treatment of relapsing‐remitting multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 2006;113(5):283‐7. - PubMed
European Study Group 1998 {published data only}
-
- European Study Group. Placebo‐controlled multicentre randomised trial of interferon beta‐1b in treatment of secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. European Study Group on interferon beta‐1b in secondary progressive MS. Lancet 1998;352(9139):1491‐7. [PUBMED: 9820296] - PubMed
EVIDENCE 2007 {published data only}
-
- Schwid S, Panitch H. Full results of the Evidence of Interferon Dose‐Response‐European North American Comparative Efficacy (EVIDENCE) study: a multicenter, randomized, assessor‐blinded comparison of low‐dose weekly versus high‐dose, high‐frequency interferon beta‐1a for relapsing multiple sclerosis. Clinical Therapeutics 2007;29(9):2031‐48. [PUBMED: 18035202] - PubMed
Fazekas 1997 {published data only}
-
- Fazekas F, Deisenhammer F, Strasser‐Fuchs S, Nahler G, Mamoli B. Randomised placebo‐controlled trial of monthly intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in relapsing‐remitting multiple sclerosis. Lancet 1997;349(9052):589‐93. - PubMed
Fazekas 2008 {published data only}
-
- Fazekas F, Lublin F, Li D, Freedman M, Hartung H, Rieckmann P, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin in relapsing‐remitting multiple sclerosis: a dose‐finding trial. Neurology 2008;71(4):265‐71. - PubMed
Ghezzi 1989 {published data only}
-
- Ghezzi A, Falco M, Locatelli C. In: Consette RE, Delmotte P editor(s). Clinical controlled randomized trial of azathioprine in multiple sclerosis. Elsevier, 1989.
Goodkin 1991 {published data only}
-
- Goodkin D, Bailly R, Teetzen M, Hertsgaard D, Beatty W. The efficacy of azathioprine in relapsing‐remitting multiple sclerosis. Neurology 1991;41:20‐5. [DOI] - PubMed
Goodkin 1995 {published data only}
-
- Goodkin D, Rudick R, VanderBrug Medendorp S, Daughtry M, Schwetz K, Fischer J, et al. Low‐dose (7.5 mg) oral methotrexate reduces the rate of progression in chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. Annals of Neurology 1995;37(1):30‐40. [PUBMED: 7818255] - PubMed
Hartung 2002 {published data only}
-
- Hartung H, Gonsette R, Konig N, Kwiecinski H, Guseo A, Morrissey S, et al. Mitoxantrone in progressive multiple sclerosis: a placebo‐controlled, double‐blind, randomised, multicentre trial. Lancet 2002;360(9350):2018‐25. [PUBMED: 12504397] - PubMed
Hommes 2004 {published data only}
-
- Hommes O, Sorensen P, Fazekas F, Enriquez M, Koelmel H, Fernandez O, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis: randomised placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet 2004;364(9440):1149‐56. - PubMed
IFNB MS Group 1993 {published data only}
-
- IFNB MSG. Interferon beta‐1b is effective in relapsing‐remitting multiple sclerosis. I. Clinical results of a multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. The IFNB Multiple Sclerosis Study Group. Neurology 1993;43(4):655‐61. [PUBMED: 8469318] - PubMed
IMPACT 2002 {published data only}
-
- Cohen J, Cutter G, Fischer J, Goodman A, Heidenreich F, Kooijmans M, et al. Benefit of interferon beta‐1a on MSFC progression in secondary progressive MS. Neurology 2002;59(5):679‐87. [PUBMED: 12221157] - PubMed
INCOMIN 2002 {published data only}
-
- Durelli L, Verdun E, Barbero P, Bergui M, Versino E, Ghezzi A, et al. Every‐other‐day interferon beta‐1b versus once‐weekly interferon beta‐1a for multiple sclerosis: results of a 2‐year prospective randomised multicentre study (INCOMIN). Lancet 2002;359:1453‐60. - PubMed
Johnson 1995 {published data only}
-
- Johnson K, Brooks B, Cohen J, Ford C, Goldstein J, Lisak R, et al. Copolymer 1 reduces relapse rate and improves disability in relapsing‐remitting multiple sclerosis: results of a phase III multicenter, double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial. The Copolymer 1 Multiple Sclerosis Study Group. Neurology 1995;45(7):1268‐76. [PUBMED: 7617181] - PubMed
Knobler 1993 {published data only}
-
- Knobler R, Greenstein J, Johnson K, Lublin F, Panitch H, Conway K, et al. Systemic recombinant human interferon‐beta treatment of relapsing‐remitting multiple sclerosis: pilot study analysis and six‐year follow‐up. Journal of Interferon Research 1993;13:333‐40. [PUBMED: 8301153] - PubMed
Koch‐Henriksen 2006 {published data only}
-
- Koch‐Henriksen N, Sørensen P, Christensen T, Frederiksen J, Ravnborg M, Jensen K, et al. A randomised study of two interferon‐beta treatments in relapsing‐remitting multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2006;66(7):1056‐60. - PubMed
Leary 2003 {published data only}
-
- Leary S, Miller D, Stevenson V, Brex P, Chard D, Thompson A. Interferon beta‐1a in primary progressive MS: an exploratory, randomized, controlled trial. Neurology 2003;60(1):44‐51. [PUBMED: 12525716] - PubMed
Lewanska 2002 {published data only}
-
- Lewanska M, Siger Zajdel M, Selmaj K. No difference in efficacy of two different doses of intravenous immunoglobulins in MS: clinical and MRI assessment. European Journal of Neurology 2002;9(6):565‐72. - PubMed
Likosky 1991 {published data only}
Milanese 1993 {published data only}
-
- Milanese C, Mantia L, Salmaggi A, Eoli M. A double blind study on azathioprine efficacy in multiple sclerosis: final report. Journal of Neurology 1993;240(5):295‐8. - PubMed
Millefiorini 1997 {published data only}
-
- Millefiorini E, Gasperini C, Pozzilli C, D'Andrea F, Bastianello S, Trojano M, et al. Randomized placebo‐controlled trial of mitoxantrone in relapsing‐remitting multiple sclerosis: 24‐month clinical and MRI outcome. Journal of Neurology 1997;244(3):153‐9. [PUBMED: 9050955] - PubMed
Miller 1961 {published data only}
-
- Miller H, Newell D, Ridley A. Multiple sclerosis. Trials of maintenance treatment with prednisolone and soluble aspirin. Lancet 1961; Vol. 1, issue 7169:127‐9. - PubMed
Montalban 2009 {published data only}
-
- Montalban X, Sastre‐Garriga J, Tintore M, Brieva L, Aymerich F, Rio J, et al. A single‐center, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of interferon beta‐1b on primary progressive and transitional multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis 2009;15(10):1195‐205. [PUBMED: 19797261] - PubMed
MSCRG 1996 {published data only}
-
- Jacobs L, Cookfair D, Rudick R, Herndon R, Richert J, Salazar A, et al. Intramuscular interferon beta‐1a for disease progression in relapsing multiple sclerosis. The Multiple Sclerosis Collaborative Research Group (MSCRG). Annals of Neurology 1996;39:285‐94. - PubMed
NASP 2004 {published data only}
-
- Panitch H, Miller A, Paty D, Weinshenker B. Interferon beta‐1b in secondary progressive MS: results from a 3‐year controlled study. Neurology 2004;63(10):1788‐95. [PUBMED: 15557491] - PubMed
OWIMS 1999 {published data only}
-
- OWIMS. Evidence of interferon beta‐1a dose response in relapsing‐remitting MS: the OWIMS Study. The Once Weekly Interferon for MS Study Group. Neurology 1999;53(4):679‐86. [PUBMED: 10489026] - PubMed
Pohlau 2007 {published data only}
-
- Pohlau D, Przuntek H, Sailer M, Bethke F, Koehler J, Konig N, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin in primary and secondary chronic progressive multiple sclerosis: a randomized placebo controlled multicentre study. Multiple Sclerosis 2007;13(9):1107‐17. [PUBMED: 17623736] - PubMed
PRISMS 1998 {published data only}
-
- PRISMS. Randomised double‐blind placebo‐controlled study of interferon beta‐1a in relapsing/remitting multiple sclerosis. PRISMS (Prevention of Relapses and Disability by Interferon beta‐1a Subcutaneously in Multiple Sclerosis) Study Group. Lancet 1998;352(9139):1498‐504. [PUBMED: 9820297] - PubMed
REGARD 2008 {published data only}
-
- Mikol D, Barkhof F, Chang P, Coyle P, Jeffery D, Schwid S, et al. Comparison of subcutaneous interferon beta‐1a with glatiramer acetate in patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis (the REbif vs Glatiramer Acetate in Relapsing MS Disease [REGARD] study): a multicentre, randomised, parallel, open‐label trial. Lancet Neurology 2008;7(10):903‐14. - PubMed
SENTINEL 2006 {published data only}
-
- Rudick R, Stuart W Calabresi P, Confavreux C, Galetta S, Radue E, et al. Natalizumab plus interferon beta‐1a for relapsing multiple sclerosis. The New England Journal of Medicine 2006;354(9):911‐23. - PubMed
SPECTRIMS 2001 {published data only}
-
- SPECTRIMS. Randomized controlled trial of interferon‐ beta‐1a in secondary progressive MS: Clinical results. Neurology 2001;56(11):1496‐504. [PUBMED: 11402106] - PubMed
Wolinsky 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wolinsky J, Narayana P, O'Connor P, Coyle P, Ford C, Johnson K, et al. Glatiramer acetate in primary progressive multiple sclerosis: results of a multinational, multicenter, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Annals of Neurology 2007;61(1):14‐24. [PUBMED: 17262850] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Arnason 1999 {published data only}
-
- Arnason, BGW, Jacobs G, Hanlon M, Harding B, Noronha ABC, Auty A, et al. TNF neutralization in MS: Results of a randomized, placebo‐controlled multicenter study. Neurology 1999;53(3):457‐65. - PubMed
Barkhof 2003 {published data only}
-
- Barkhof F, Rocca M, Francis G, Waesberghe JH, Uitdehaag BM, Hommes OR, et al. Validation of diagnostic magnetic resonance imaging criteria for multiple sclerosis and response to interferon beta 1a. Annals of Neurology 2003;53(3):718‐24. - PubMed
Baum 2006 {published data only}
-
- Baum K, Mannitol Formulation Study Group. Safety and tolerability of a 'refrigeration‐free' formulation of interferon beta‐1b‐‐results of a double‐blind, multicentre, comparative study in patients with relapsing‐remitting or secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. The Journal of International Medical Research 2006;34(1):1‐12. - PubMed
BENEFIT 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kappos L, Polman C, Freedman M, Edan G, Hartung H, Miller D, et al. Treatment with interferon beta‐1b delays conversion to clinically definite and McDonald MS in patients with clinically isolated syndromes. Neurology 2006;67(7):1242‐9. - PubMed
Boiko 2001 {published data only}
-
- Boiko A, Skurkovich S, Buglak A, Alekseeva, T, Smirnova N, Skurkovich B, et al. Randomized, placebo‐controlled trial comparing short course of anti‐IFN? And anti‐TNFa showed only anti‐IFN? Effective in secondary progressive MS. Journal of Neurosurgery 2001;187 Suppl 1:S456.
Burton 2009 {published data only}
CHAMPS 2000 {published data only}
-
- Jacobs L, Beck R, Simon J, Kinkel R, Brownscheidle C, Murray T, et al. Intramuscular interferon beta‐1a therapy initiated during a first demyelinating event in multiple sclerosis. CHAMPS Study Group. The New England Journal of Medicine 2000;343(13):898‐904. [PUBMED: 11006365] - PubMed
Christodoulou 2006 {published data only}
-
- Christodoulou C, Melville P, Scherl WF, MacAllister WS, Elkins LE, Krupp LB. Effects of donepezil on memory and cognition in multiple sclerosis. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2006;245(1‐2):127‐36. - PubMed
Clanet 2002 {published data only}
-
- Clanet M, Radue E, Kappos L, Hartung H, Hohlfeld R, Sandberg‐Wollheim M, et al. A randomized, double‐blind, dose‐comparison study of weekly interferon beta‐1a in relapsing MS. Neurology 2002;59(10):1507‐17. [PUBMED: 12451189] - PubMed
Durelli 1994 {published data only}
-
- Durelli L, Bongioanni M, Cavallo R, Ferrero B, Ferri R, Ferrio M, et al. Chronic systemic high‐dose recombinant interferon alfa‐2a reduces exacerbation rate, MRI signs of disease activity, and lymphocyte interferon gamma production in relapsing‐remitting multiple sclerosis. Neurology 1994;44(3 (Pt 1)):406‐13. - PubMed
ETOMS 2001 {published data only}
-
- Comi G, Filippi M, Barkhof F, Durelli L, Edan G, Fernández O, et al. Effect of early interferon treatment on conversion to definite multiple sclerosis: a randomised study. Lancet 2001;357(9268):1576‐82. - PubMed
Fernandez 2002 {published data only}
-
- Fernandez O, Guerrero M, Mayorga C, Munoz L, Lean A, Luque G, et al. Combination therapy with interferon beta‐1b and azathioprine in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. A two‐year pilot study. Journal of Neurology 2002;249(8):1058‐62. - PubMed
Filippi 2004 {published data only}
-
- Filippi M, Rovaris M, Inglese M, Barkhof F, Stefano N, Smith S, et al. Interferon beta‐1a for brain tissue loss in patients at presentation with syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis: a randomised, double blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Lancet 2004;364(9444):1489‐96. - PubMed
Filippi 2006 {published data only}
-
- Filippi M, Wolinsky J, Comi G. Effects of oral glatiramer acetate on clinical and MRI‐monitored disease activity in patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis: a multicentre, double‐blind, randomised, placebo‐controlled study. Lancet Neurology 2006;5:213‐20. - PubMed
GLANCE 2009 {published data only}
Goodkin 2000 {published data only}
-
- Goodkin DE, Shulman M, Winkelhake J, Waubant E, Andersson P, Stewart T, et al. A phase I trial of solubilized DR2:MBP84‐102 (AG284) in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2000;54(7):1414. - PubMed
Hauser 1983 {published data only}
-
- Hauser S, Dawson D, Lehrich J, Beal M, Kevy S, Propper R, et al. Intensive immunosuppression in progressive multiple sclerosis. A randomized, three‐arm study of high‐dose intravenous cyclophosphamide, plasma exchange and ACTH [comment in: N Engl J Med 1983;309:239‐40; comment in: N Engl J Med 1983;309:241; comment in: Lancet 1991;337:1540‐1]. The New England Journal of Medicine 1983;308(4):173‐80. - PubMed
Hoogervorst 2002 {published data only}
-
- Hoogervorst EL, Polman CH, Barkhof F. Cerebral volume changes in multiple sclerosis patients treated with high‐dose intravenous methylprednisolone. Multiple Sclerosis 2002;8(5):415‐9. - PubMed
Labetouelle 2001 {published data only}
-
- Labetouelle M. [About the article: " Intramuscular interferon beta‐1a therapy initiated during a first demyelinating event in multiple sclerosis" by Jacobs LD et al]. Journal Francais of Ophthalmology 2001;24(2):222. - PubMed
Liu 2010 {published data only}
Myhr 1999 {published data only}
-
- Myhr K, Riise T, Green L, Beiske T, Celius E, Edland A, et al. Interferon‐alpha2a reduces MRI disease activity in relapsing‐remitting multiple sclerosis. Norwegian Study Group on Interferon‐alpha in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurology 1999;52(5):1049‐56. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Patti 1999 {published data only}
-
- Patti F, L'Episcopo MR, Cataldi ML, Reggio A. Natural interferon‐beta treatment of relapsing‐remitting and secondary‐progressive multiple sclerosis patients. A two‐year study. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 1999;100(5):283‐9. - PubMed
Rio 2007 {published data only}
-
- Río J, Tintoré M, Nos C, Téllez N, Galán I, Pelayo R, et al. Interferon beta in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Daily clinical practice. Journal of Neurology 2007;254:849–53. - PubMed
Skurkovich 2001 {published data only}
-
- Skurkovich S, Boiko A, Beliaeva I, Buglak A, Alekseeva T, Smirnova N, et al. Randomized study of antibodies to IFN‐gamma and TNF‐alpha in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis 2001;7(5):277‐84. - PubMed
Steultjens 2003 {published data only}
Tejani 2010 {published data only}
Tubridy 1999 {published data only}
-
- Tubridy N, Behan PO, Capildeo R, Chaudhuri A, Forbes R, Hawkins CP, et al. The effect of anti‐[alpha]4 integrin antibody on brain lesion activity in MS. Neurology 1999;53(3):466‐72. - PubMed
Van de Wyngaert 2001 {published data only}
-
- Wyngaert F, Beguin C, D'Hooghe M, Dooms G, Lissoir F, Carton H, et al. A double‐blind clinical trial of mitoxantrone versus methylprednisolone in relapsing, secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurologica Belgica 2001;101(4):210‐6. - PubMed
Wender 1988 {published data only}
-
- Wender M, Tokarz‐Kupczyk E, Mularek O. Early results of the treatment of chronic progressive forms of multiple sclerosis with cyclophosphamide and ACTH [Wczesne wyniki leczenia postaci przewlekle postepujacych stwardnienia rozsianego cyklofosfamidem i ACTH]. Neurologia i Neurochirurgia Polska 1988;22(5):399‐403. - PubMed
Zavalishin 2003 {published data only}
-
- Zavalishin IA, Gusev EI, Iakhno NN, Skoromets AA, Ko AN, Demina TL, et al. Results of a multicenter study of Rebif‐22 mcg administration in Russia. Zhurnal Nevrologii i Psikhiatrii Imeni S.S. Korsakova / Ministerstvo zdravookhraneniia i meditsinskoi promyshlennosti Rossiiskoi Federatsii, Vserossiiskoe obshchestvo nevrologov [i] Vserossiiskoe obshchestvo psikhiatrov 2003;Spec No 2:S73‐8.
Zivadinov 2001 {published data only}
-
- Zivadinov R, Rudick R, Masi R, Nasuelli D, Ukmar M, et al. Effects of IV methylprednisolone on brain atrophy in relapsing‐remitting MS. Neurology 2001;57(7):1239‐47. - PubMed
Additional references
Association of British Neurologists 2005
-
- Association of British Neurologists 2005. Guidelines for the Use of Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Neurological Diseases. www.theabn.org/documents/IVIg‐Guidelines 2005. [OTHER]
Bennett 2009
-
- Bennett J, Stüve O. Update on inflammation, neurodegeneration, and immunoregulation in multiple sclerosis: therapeutic implications. Clinical Neuropharmacology 2009;32(3):121‐32. - PubMed
Billiau 2004
-
- Billiau A, Kieseier B, Hartung H. Biologic role of interferon beta in multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurology 2004;251 Suppl 2:II10‐4. - PubMed
Birnbaum 2008
-
- Birnbaum G, Cree B, Altafullah I, Zinser M, Reder A. Combining beta interferon and atorvastatin may increase disease activity in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2008;71(18):1390‐5. - PubMed
Bloomgren 2012
-
- Bloomgren G, Richman S, Hotermans C, Subramanyam M, Goelz S, Natarajan A, et al. Risk of natalizumab‐associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. The New England journal of medicine 2012;366(20):1870‐80. - PubMed
Byrnes 2006
-
- V Byrnes, N Afdhal, T Challies, PE Greenstein. Drug induced liver injury secondary to interferon‐beta (IFN‐ β) in multiple sclerosis. Annals of Hepatology 2006;5(1):56‐9. - PubMed
Calabresi 1991
-
- Calabresi P, Chabner B. Antineoplastic agents. In: Goodman, Gillman's. Hardman JG Limbird LE, Molinoff PB, Ruddon RW, Goodman Gillman A editor(s). Goodman & Gillman's. The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. Eighth. Vol. II, New York: Pergamon Press, 1991:1209‐23.
Caldwell 2005
Casetta 2007
Chaimani 2012
-
- Chaimani A, Salanti G. Using network meta‐analysis to evaluate the existence of small‐study effects in a network of interventions. Res Synth Method 2012;3:161‐176. - PubMed
Ciccone 2008
Compston 2002
-
- Compston A, Coles A. Multiple sclerosis. Lancet 2002;359:1221‐31. - PubMed
Daumer 2009
-
- Daumer M, Neuhaus A, Morrissey S, Hintzen R, Ebers G. MRI as an outcome in multiple sclerosis clinical trials. Neurology 2009;72:705‐11. - PubMed
Del Giovane 2013
-
- Giovane C, Vacchi L, Mavridis D, Filippini G, Salanti G. Network meta‐analysis models to account for variability in treatment definitions: application to dose effects. Statistics in Medicine 2013;32(1):25‐39. - PubMed
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7:177‐88. - PubMed
Ebers 2006
-
- Ebers G. Disease evolution in multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurology 2006;253 Suppl 6:3–8.
Ebers 2008
-
- Ebers G, Heigenhauser L, Daumer M, Lederer C, Noseworthy J. Disability as an outcome in MS clinical trials. Neurology 2008;71:624‐31. - PubMed
Elovaara 2008
-
- Elovaara I, Apostolski S, Doorn P, Gilhus N, Hietaharju A, Honkaniemi J, et al. EFNS guidelines for the use of intravenous immunoglobulin in treatment of neurological diseases: EFNS task force on the use of intravenous immunoglobulin in treatment of neurological diseases. European Journal of Neurology 2008;15(9):893‐908. - PubMed
EMEA 2002
-
- European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products. Committee for Proprietary Medicinal Products European Public Assessment Report (EPAR): Betaferon. London: EMEA 2002.
FDA 1993
-
- U.S. Food, Drug Administration. Betaseron Interferon BETA‐1B Subcutaneous. Drug Approval Package‐ Licensing Action 07/23/1993. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/pre96/103471s0000TOC.cfm.
FDA 1996
-
- U.S. Food, Drug Administration. Glatiramer acetate (Copaxone) Product Approval Information Licensing Action 12/20/1996. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/index.cfm?fuseacti....
FDA 2000
-
- U.S. Food, Drug Administration. Mitoxantrone (Novantrone) Product Approval Information ‐ Licensing Action Approval Date: 1/28/2000. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/Scripts/cder/DrugsatFDA/index.cfm?fuseacti....
FDA 2001
-
- U.S. Food, Drug Administration. Interferon 1b (Betaseron) treatment of secondary progressive forms of multiple sclerosis. Clinical review of the June 28, 2000 amendment to supplemental BLA 98‐0737 ‐‐ STN103471. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/HowDrugsar... (accessed 17 Feb 2011).
FDA 2002
-
- U.S. Food, Drug Administration. Interferon beta‐1a (Rebif) Product Approval Information ‐ Licensing Action Approval Date: 3/7/2002. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/HowDrugsareDeveloped....
FDA 2003
-
- U.S. Food, Drug Administration. Food and Drug Administration. Interferon beta‐1a (AVONEX)Product Approval Information ‐ Licensing Action 5/28/03. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/HowDrugsareDeveloped....
FDA 2004
-
- U.S. Food, Drug Administration. Tysabri (Natalizumab) Approval Date: 11/23/2004. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2004/125104s000_Natali....
FDA 2005
-
- U.S. Food, Drug Administration. Mitoxantrone Hydrochloride (marketed as Novantrone and generics) ‐ Healthcare Professional Sheet text version. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/PostmarketDrugSafetyInformationforPa... (accessed November 2011).
FDA 2011
-
- U.S. Food, Drug Administration. COPAXONE® (glatiramer acetate injection) solution for subcutaneous injection. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformati... (accessed September 2012).
Filippini 2007
-
- Filippini G, Ebers G. Multiple sclerosis: critical review of the evidence for each question. In: Candelise L, Hughes R, Liberati A, Uitdehaag BMJ, Warlow C editor(s). Evidence‐Based Neurology. Management of neurological disorders. 1st Edition. Blackwell Publishing, 2007:221‐33.
Fontoura 2010
Fox 2004
-
- Fox E. Mechanism of action of mitoxantrone. Neurology 2004;63(12):S15‐8. - PubMed
Fragoso 2010
-
- Fragoso Y, Frota E, Lopes J, Noal J, Giacomo M, Gomes S, et al. Severe depression, suicide attempts, and ideation during the use of interferon beta by patients with multiple sclerosis. Clinical Neuropharmacology 2010;33(6):312‐6. - PubMed
Fragoso 2011
-
- Fragoso Y, Paggiaro M, Mastromauro R, Silva Jacondino G, Wilson H. Literature systematic review on the ophthalmological side effects of interferons. Arquivos Brasileiros de Oftalmologia 2011;74(4):306‐10. - PubMed
Glenny 2005
-
- Glenny A, Altman D, Song F, Sakarovitch C, Deeks J, D'Amico R, et al. Indirect comparisons of competing interventions. Health Technology Assessment 2005;9:1‐34. - PubMed
Goodin 2002
-
- Goodin D, Frohman E, Garmany G, Halper J, Likosky W, Lublin F, et al. Disease modifying therapies in multiple sclerosis: report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the MS Council for Clinical Practice Guidelines. Neurology 2002;58(2):169‐78. - PubMed
Goodman 2009
Gray 2003
Gray 2004
Higgins 1996
-
- Higgins J, Whitehead A. Borrowing strength from external trials in a meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 1996;15(24):2733‐49. [PUBMED: 8981683] - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins J, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011] . Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Johnston 2005
-
- Johnston A, Gudjonsson J, Sigmundsdottir H, Runar L, Valdimarsson H. The anti‐inflammatory action of methotrexate is not mediated by lymphocyte apoptosis, but by the suppression of activation and adhesion molecules. Clinical Immunology 2005;114(2):154‐63. - PubMed
Khoury 2010
Kremenchutzky 2006
-
- Kremenchutzky M, Rice G, Baskerville J, Wingerchuk D, Ebers G. The natural history of multiple sclerosis: a geographically based study. 9. Observations on the progressive phase of the disease. Brain 2006;129:584‐94. - PubMed
Kurtzke 1983
-
- Kurtzke J. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 1983;33:1444‐52. - PubMed
La Mantia 2007
La Mantia 2010
La Mantia 2012
Lalive 2011
Le Page 2011
-
- Page E, Leray E, Edan G, French Mitoxantrone Safety Group. Long‐term safety profile of mitoxantrone in a French cohort of 802 multiple sclerosis patients: a 5‐year prospective study. Multiple Sclerosis 2011;17(7):867‐75. - PubMed
Lu 2004
-
- Lu G, Ades A. Combination of direct and indirect evidence in mixed treatment comparisons. Statistics in Medicine 2004;23(20):3105‐24. - PubMed
Lu 2006
-
- Lu G, Ades A. Assessing evidence inconsistency in mixed treatment comparisons. Journal of American Statistical Association 2006;101:447‐59.
Lublin 1996
-
- Lublin F, Reingold S. Defining the clinical course of multiple sclerosis: results of an international survey. National Multiple Sclerosis Society (USA) Advisory Committee on Clinical Trials of New Agents in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurology 1996;46:907‐11. - PubMed
Martinelli 2005
McDonald 2001
-
- McDonald W, Compston A, Edan G, Goodkin D, Hartung H, Lublin F. Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the international panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Annals of Neurology 2001;50:121‐7. - PubMed
Milo 2010
-
- Milo R, Kahana R. Multiple sclerosis: geoepidemiology, genetics and the environment. Autoimmune Reviews 2010;9(5):A387‐94. - PubMed
Nabavi 2011
Nakamura 2008
-
- Nakamura Y, Kawachi Y, Furuta J, Otsuka F. Severe local skin reactions to interferon beta‐1b in multiple sclerosis‐improvement by deep subcutaneous injection. European Journal of Dermatology 2008;18(5):579‐82. - PubMed
Nonchev 2010
-
- Nonchev B. Cases of interferon‐alpha and interferon‐beta‐induced thyroiditis. Folia Medica (Plovdiv) 2010;52(3):5‐12. - PubMed
Polman 2005
-
- Polman C, Reingold S, Edan G, Filippi M, Hartung H, Kappos L, et al. Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2005 revisions to the 'McDonald Criteria'. Annals of Neurology 2005;58:840‐6. - PubMed
Poser 1983
-
- Poser C, Paty D, Scheinberg L, McDonald W, Davis F, Ebers G, et al. New diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines for research protocols. Annals of Neurology 1983;13:227‐31. - PubMed
Pozzilli 2004
-
- Pozzilli C, Marinelli F, Romano S, Bagnato F. Corticosteroids treatment. Journal of Neurological Sciences 2004;223(1):47‐51. - PubMed
Pucci 2011
Ravnborg 2010
-
- Ravnborg M, Sørensen P, Andersson M, Celius E, Jongen P, Elovaara I, et al. Methylprednisolone in combination with interferon beta‐1a for relapsing‐remitting multiple sclerosis (MECOMBIN study): a multicentre, double‐blind, randomised, placebo‐controlled, parallel‐group trial. Lancet Neurology 2010;9:672–80. - PubMed
Rice 2001
Rojas 2010
Salanti 2008
-
- Salanti G, Higgins J, Ades A, Ioannidis J. Evaluation of networks of randomized trials. Statistical Methods in Medical Research 2008;17:279‐301. - PubMed
Salanti 2009
-
- Salanti G, Marinho V, Higgins J. A case study of multiple‐treatments meta‐analysis demonstrates that covariates should be considered. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2009;62:857‐64. - PubMed
Salanti 2011
-
- Salanti G, Ades A, Ioannidis J. Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple‐treatment meta‐analysis: an overview and tutorial. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64:163‐71. - PubMed
Schünemann 2011a
-
- Schünemann H, Oxman A, Higgins J, Vist G, Glasziou P, Guyatt G. Chapter 11: Presenting results and ‘Summary of findings’ tables. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org, Version 5.0.1 (updated March 2011).
Schünemann 2011b
-
- Schünemann H, Oxman A, Vist G, Higgins J, Deeks J, Glasziou P, et al. Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org, Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011).
Shirani 2012
-
- Shirani A, Zhao Y, Karim M, Evans C, Kingwell E, Kop M, et al. Association between use of interferon beta and progression of disability in patients with relapsing‐remitting multiple sclerosis. JAMA 2012;308(3):247‐56. [OTHER] - PubMed
Sloka 2005
-
- Sloka J, Stefanelli M. The mechanism of action of methylprednisolone in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis 2005;11:425‐32. - PubMed
Smith 2010
-
- Smith B, Susan C, Rochelle F, Marian M, Tracy D, Benjamin K, et al. Drug class review: disease‐modifying drugs for multiple sclerosis: final update 1 report [Internet]. Portland (OR): Oregon Health & Science University, 2010. [Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK50570/] - PubMed
Spiegelhalter 2002
-
- Spiegelhalter D, Best N, Carlin B, Linde A. Bayesian measures of model complexity and fit. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society 2002;64:583‐616.
Stangel 1999
-
- Stangel M, Toyka K, Gold R. Mechanisms of high‐dose intravenous immunoglobulins in demyelinating diseases. Archives of Neurology 1999;56(6):661‐3. - PubMed
Tiede 2003
Vercellino 2009
-
- Vercellino M, Masera S, Lorenzatti M, Condello C, Merola A, Mattioda A, et al. Demyelination, inflammation and neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis deep gray matter. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 2009;68:489‐502. - PubMed
Weiner 1993
-
- Weiner H, Mackin G, Matsui M, Orav E, Khoury S, Dawson D, et al. Double‐blind pilot trial of oral tolerization with myelin antigens in multiple sclerosis. Science 1993;259(5099):1321‐4. - PubMed
Yousry 2006
Zintzaras 2012
-
- Zintzaras E, Doxani C, Mprotsis T, Schmid CH, Hadjigeorgiou G. Network analysis of randomized controlled trials in multiple sclerosis. Clinical Therapeutics 2012;34(4):857‐69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

