Ribosomal and hematopoietic defects in induced pluripotent stem cells derived from Diamond Blackfan anemia patients
- PMID: 23744582
- PMCID: PMC3739037
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2013-01-478321
Ribosomal and hematopoietic defects in induced pluripotent stem cells derived from Diamond Blackfan anemia patients
Abstract
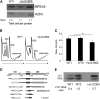
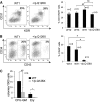
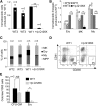
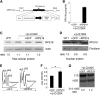
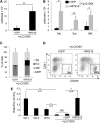
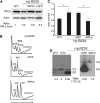
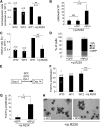
Diamond Blackfan anemia (DBA) is a congenital disorder with erythroid (Ery) hypoplasia and tissue morphogenic abnormalities. Most DBA cases are caused by heterozygous null mutations in genes encoding ribosomal proteins. Understanding how haploinsufficiency of these ubiquitous proteins causes DBA is hampered by limited availability of tissues from affected patients. We generated induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) from fibroblasts of DBA patients carrying mutations in RPS19 and RPL5. Compared with controls, DBA fibroblasts formed iPSCs inefficiently, although we obtained 1 stable clone from each fibroblast line. RPS19-mutated iPSCs exhibited defects in 40S (small) ribosomal subunit assembly and production of 18S ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Upon induced differentiation, the mutant clone exhibited globally impaired hematopoiesis, with the Ery lineage affected most profoundly. RPL5-mutated iPSCs exhibited defective 60S (large) ribosomal subunit assembly, accumulation of 12S pre-rRNA, and impaired erythropoiesis. In both mutant iPSC lines, genetic correction of ribosomal protein deficiency via complementary DNA transfer into the "safe harbor" AAVS1 locus alleviated abnormalities in ribosome biogenesis and hematopoiesis. Our studies show that pathological features of DBA are recapitulated by iPSCs, provide a renewable source of cells to model various tissue defects, and demonstrate proof of principle for genetic correction strategies in patient stem cells.
Figures
Comment in
-
Defects in DBA: more than meets the eye.Blood. 2013 Aug 8;122(6):856-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-06-508465. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23929834
References
-
- Ball S. Diamond Blackfan anemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2011;2011:487-491. - PubMed
-
- Gazda HT, Zhong R, Long L, et al. RNA and protein evidence for haplo-insufficiency in Diamond-Blackfan anaemia patients with RPS19 mutations. Br J Haematol. 2004;127(1):105–113. - PubMed
-
- Ellis SR, Gleizes PE. Diamond Blackfan anemia: ribosomal proteins going rogue. Semin Hematol. 2011;48(2):89–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

