Minireview: Dopaminergic regulation of insulin secretion from the pancreatic islet
- PMID: 23744894
- PMCID: PMC3725340
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2013-1083
Minireview: Dopaminergic regulation of insulin secretion from the pancreatic islet
Abstract
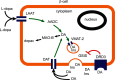
Exogenous dopamine inhibits insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells, but the lack of dopaminergic neurons in pancreatic islets has led to controversy regarding the importance of this effect. Recent data, however, suggest a plausible physiologic role for dopamine in the regulation of insulin secretion. We review the literature underlying our current understanding of dopaminergic signaling that can down-regulate glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from pancreatic islets. In this negative feedback loop, dopamine is synthesized in the β-cells from circulating L-dopa, serves as an autocrine signal that is cosecreted with insulin, and causes a tonic inhibition on glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. On the whole animal scale, L-dopa is produced by cells in the gastrointestinal tract, and its concentration in the blood plasma increases following a mixed meal. By reviewing the outcome of certain types of bariatric surgery that result in rapid amelioration of glucose tolerance, we hypothesize that dopamine serves as an "antiincretin" signal that counterbalances the stimulatory effect of glucagon-like peptide 1.
Figures
References
-
- Takamine J. Adrenalin the active principle of the supra-renal glands and its mode of preparation. Amer J Pharm. 1901;73:523–531
-
- Aldrich T. A preliminary report on the active principle of the suprarenal gland. Am J Physiol. 1901;5:457–461
-
- Carlsson A, Lindqvist M, Magnusson T. 3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine and 5-hydroxytryptophan as reserpine antagonists. Nature. 1957;180:1200. - PubMed
-
- Winzell MS, Ahrén B. G-protein-coupled receptors and islet function-implications for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Pharmacol Ther. 2007;116:437–448 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

