Fortuitously discovered liver lesions
- PMID: 23745019
- PMCID: PMC3671069
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i21.3173
Fortuitously discovered liver lesions
Abstract
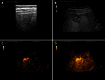
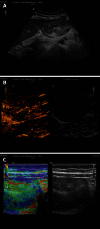
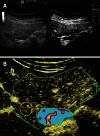
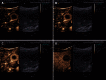
The fortuitously discovered liver lesion is a common problem. Consensus might be expected in terms of its work-up, and yet there is none. This stems in part from the fact that there is no preventive campaign involving the early detection of liver tumors other than for patients with known liver cirrhosis and oncological patients. The work-up (detection and differential diagnosis) of liver tumors comprises theoretical considerations, history, physical examination, laboratory tests, standard ultrasound, Doppler ultrasound techniques, contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS), computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, as well as image-guided biopsy. CEUS techniques have proved to be the most pertinent method; these techniques became part of the clinical routine about 10 years ago in Europe and Asia and are used for a variety of indications in daily clinical practice. CEUS is in many cases the first and also decisive technical intervention for detecting and characterizing liver tumors. This development is reflected in many CEUS guidelines, e.g., in the European Federation of Societies for Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology (EFSUMB) guidelines 2004, 2008 and 2012 as well as the recently published World Federation for Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology-EFSUMB guidelines 2012. This article sets out considerations for making a structured work-up of incidental liver tumors feasible.
Keywords: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound; Focal nodular hyperplasia; Guidelines; Hemangioma; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Metastasis; Recommendations; Ultrasonography.
Figures


References
-
- Albrecht T, Blomley M, Bolondi L, Claudon M, Correas JM, Cosgrove D, Greiner L, Jäger K, Jong ND, Leen E, et al. Guidelines for the use of contrast agents in ultrasound. January 2004. Ultraschall Med. 2004;25:249–256. - PubMed
-
- Claudon M, Cosgrove D, Albrecht T, Bolondi L, Bosio M, Calliada F, Correas JM, Darge K, Dietrich C, D’Onofrio M, et al. Guidelines and good clinical practice recommendations for contrast enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) - update 2008. Ultraschall Med. 2008;29:28–44. - PubMed
-
- Piscaglia F, Nolsøe C, Dietrich CF, Cosgrove DO, Gilja OH, Bachmann Nielsen M, Albrecht T, Barozzi L, Bertolotto M, Catalano O, et al. The EFSUMB Guidelines and Recommendations on the Clinical Practice of Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS): update 2011 on non-hepatic applications. Ultraschall Med. 2012;33:33–59. - PubMed
-
- Claudon M, Dietrich CF, Choi BI, Cosgrove DO, Kudo M, Nolsøe CP, Piscaglia F, Wilson SR, Barr RG, Chammas MC, et al. Guidelines and good clinical practice recommendations for contrast enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) in the liver--update 2012: a WFUMB-EFSUMB initiative in cooperation with representatives of AFSUMB, AIUM, ASUM, FLAUS and ICUS. Ultraschall Med. 2013;34:11–29. - PubMed
-
- Claudon M, Dietrich CF, Choi BI, Cosgrove DO, Kudo M, Nolsøe CP, Piscaglia F, Wilson SR, Barr RG, Chammas MC, et al. Guidelines and good clinical practice recommendations for Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) in the liver - update 2012: A WFUMB-EFSUMB initiative in cooperation with representatives of AFSUMB, AIUM, ASUM, FLAUS and ICUS. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2013;39:187–210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

