The role of dynamic infrared imaging in melanoma diagnosis
- PMID: 23745131
- PMCID: PMC3670775
- DOI: 10.1586/edm.13.15
The role of dynamic infrared imaging in melanoma diagnosis
Abstract
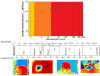
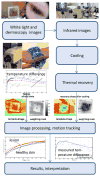
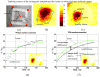
Melanoma incidence and the lifetime risk are increasing at an alarming rate in the United States and worldwide. In order to improve survival rates, the goal is to detect melanoma at an early stage of the disease. Accurate, sensitive and reliable quantitative diagnostic tools can reduce the number of unnecessary biopsies, the associated morbidity as well as the costs of care in addition to improving survival rates. The recently introduced quantitative dynamic infrared imaging system QUAINT measures differences in the infrared emission between healthy tissue and the lesion during the thermal recovery process after the removal of a cooling stress. Results from a clinical study suggest that the temperature of cancerous lesions is higher during the first 45-60 seconds of thermal recovery than the temperature of benign pigmented lesions. This small temperature difference can be measured by modern infrared cameras and serve as an indicator for melanoma in modern quantitative melanoma detectors.
Keywords: Melanoma detection; infrared cameras; infrared imaging; quantitative imaging; thermal recovery; thermostimulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection theory for accurate and non-invasive skin cancer diagnosis using dynamic thermal imaging.Biomed Opt Express. 2017 Mar 22;8(4):2301-2323. doi: 10.1364/BOE.8.002301. eCollection 2017 Apr 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2017. PMID: 28736673 Free PMC article.
-
Role of In Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy in the Analysis of Melanocytic Lesions.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018 Apr;26(1):64-67. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018. PMID: 29782304 Review.
-
Quantitative visualization and detection of skin cancer using dynamic thermal imaging.J Vis Exp. 2011 May 5;(51):2679. doi: 10.3791/2679. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 21587160 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal analysis of cancerous breast model.Int Mech Eng Congress Expo. 2012;2012:134-143. doi: 10.1115/IMECE2012-88244. Int Mech Eng Congress Expo. 2012. PMID: 25328914 Free PMC article.
-
Update and clinical use of imaging technologies for pigmented lesions of the skin.Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2012 Mar;31(1):38-44. doi: 10.1016/j.sder.2011.12.003. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2012. PMID: 22361288 Review.
Cited by
-
An Infrared Absorbance Sensor for the Detection of Melanoma in Skin Biopsies.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Oct 10;16(10):1659. doi: 10.3390/s16101659. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27735858 Free PMC article.
-
Intraoperative thermal infrared imaging in neurosurgery: machine learning approaches for advanced segmentation of tumors.Phys Eng Sci Med. 2023 Mar;46(1):325-337. doi: 10.1007/s13246-023-01222-x. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Phys Eng Sci Med. 2023. PMID: 36715852 Free PMC article.
-
Medical infrared thermography as hidradenitis suppurativa diagnostic tool: literature review.Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021 Feb;38(2):32-35. doi: 10.5114/ada.2021.104274. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021. PMID: 34408563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection theory for accurate and non-invasive skin cancer diagnosis using dynamic thermal imaging.Biomed Opt Express. 2017 Mar 22;8(4):2301-2323. doi: 10.1364/BOE.8.002301. eCollection 2017 Apr 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2017. PMID: 28736673 Free PMC article.
-
Infrared thermal modulation endoscopy for label-free tumor detection.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):31575. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76173-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;59(4):225–249. - PubMed
-
- Jones BF. A reappraisal of the use of infrared thermal image analysis in medicine. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1998;17 (6):1019–1027. - PubMed
-
- Anbar M. Clinical thermal imaging today—shifting from phenomenological thermography to pathophysiologically based thermal imaging. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag. 1998;17 (4):25–33. - PubMed
-
- Anbar M. Assessment of physiologic and pathologic radiative heat dissipation using dynamic infrared imaging. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2002;972:111–118. - PubMed
-
- Ring EFJ. Progress in the measurement of human body temperature. IEEE Eng Med Bio Mag. 1998;17:19–24. - PubMed
Websites
-
- National Cancer Institute. SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Melanoma of the Skin. http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/melan.html.
-
- Skin Cancer Foundation website. 2010 http://www.skincancer.org/Skin-Cancer-Facts/
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
