Toward a cross-species understanding of empathy
- PMID: 23746460
- PMCID: PMC3839944
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2013.04.009
Toward a cross-species understanding of empathy
Abstract
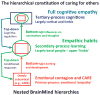
Although signs of empathy have now been well documented in non-human primates, only during the past few years have systematic observations suggested that a primal form of empathy exists in rodents. Thus, the study of empathy in animals has started in earnest. Here we review recent studies indicating that rodents are able to share states of fear, and highlight how affective neuroscience approaches to the study of primary-process emotional systems can help to delineate how primal empathy is constituted in mammalian brains. Cross-species evolutionary approaches to understanding the neural circuitry of emotional 'contagion' or 'resonance' between nearby animals, together with the underlying neurochemistries, may help to clarify the origins of human empathy.
Keywords: affective neuroscience; anterior cingulate cortex; contagion; emotion; reciprocity; rodent; social behavior.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Davis MH. Empathy: A Social Psychological Approach. Brown and Benchmark; 1994.
-
- de Vignemont F, Singer T. The empathic brain: how, when and why? Trends Cogn Sci. 2006;10:435–441. - PubMed
-
- Bernhardt BC, Singer T. The neural basis of empathy. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2012;35:1–23. - PubMed
-
- Decety J, et al. A neurobehavioral evolutionary perspective on the mechanisms underlying empathy. Prog Neurobiol. 2012;98:38–48. - PubMed
-
- Singer T, Lamm C. The social neuroscience of empathy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009;1156:81–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

