Cross-species mechanical fingerprinting of cardiac myosin binding protein-C
- PMID: 23746519
- PMCID: PMC3672900
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.04.027
Cross-species mechanical fingerprinting of cardiac myosin binding protein-C
Abstract
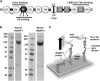
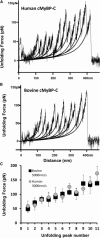
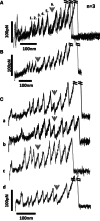
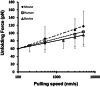
Cardiac myosin binding protein-C (cMyBP-C) is a member of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily of proteins and consists of 8 Ig- and 3 fibronectin III (FNIII)-like domains along with a unique regulatory sequence referred to as the MyBP-C motif or M-domain. We previously used atomic force microscopy to investigate the mechanical properties of murine cMyBP-C expressed using a baculovirus/insect cell expression system. Here, we investigate whether the mechanical properties of cMyBP-C are conserved across species by using atomic force microscopy to manipulate recombinant human cMyBP-C and native cMyBP-C purified from bovine heart. Force versus extension data obtained in velocity-clamp experiments showed that the mechanical response of the human recombinant protein was remarkably similar to that of the bovine native cMyBP-C. Ig/Fn-like domain unfolding events occurred in a hierarchical fashion across a threefold range of forces starting at relatively low forces of ~50 pN and ending with the unfolding of the highest stability domains at ~180 pN. Force-extension traces were also frequently marked by the appearance of anomalous force drops suggestive of additional mechanical complexity such as structural coupling among domains. Both recombinant and native cMyBP-C exhibited a prominent segment ~100 nm-long that could be stretched by forces <50 pN before the unfolding of Ig- and FN-like domains. Combined with our previous observations of mouse cMyBP-C, these results establish that although the response of cMyBP-C to mechanical load displays a complex pattern, it is highly conserved across species.
Copyright © 2013 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Offer G., Moos C., Starr R. A new protein of the thick filaments of vertebrate skeletal myofibrils. Extractions, purification and characterization. J. Mol. Biol. 1973;74:653–676. - PubMed
-
- Stelzer J.E., Patel J.R., Moss R.L. Protein kinase A-mediated acceleration of the stretch activation response in murine skinned myocardium is eliminated by ablation of cMyBP-C. Circ. Res. 2006;99:884–890. - PubMed
-
- Xu Q., Dewey S., Gomes A.V. Malignant and benign mutations in familial cardiomyopathies: insights into mutations linked to complex cardiovascular phenotypes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2010;48:899–909. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

