Cyclic GMP-AMP containing mixed phosphodiester linkages is an endogenous high-affinity ligand for STING
- PMID: 23747010
- PMCID: PMC3808999
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.05.022
Cyclic GMP-AMP containing mixed phosphodiester linkages is an endogenous high-affinity ligand for STING
Abstract
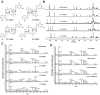
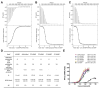
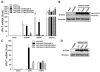
The presence of microbial or self DNA in the cytoplasm of mammalian cells is a danger signal detected by the DNA sensor cyclic-GMP-AMP (cGAMP) synthase (cGAS), which catalyzes the production of cGAMP that in turn serves as a second messenger to activate innate immune responses. Here we show that endogenous cGAMP in mammalian cells contains two distinct phosphodiester linkages, one between 2'-OH of GMP and 5'-phosphate of AMP, and the other between 3'-OH of AMP and 5'-phosphate of GMP. This molecule, termed 2'3'-cGAMP, is unique in that it binds to the adaptor protein STING with a much greater affinity than cGAMP molecules containing other combinations of phosphodiester linkages. The crystal structure of STING bound to 2'3'-cGAMP revealed the structural basis of this high-affinity binding and a ligand-induced conformational change in STING that may underlie its activation.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
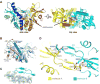

References
-
- GUSSI. on World Wide Web http://biophysicsswmededu/MBR/softwarehtml.
-
- Barber GN. Cytoplasmic DNA innate immune pathways. Immunological reviews. 2011;243:99–108. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

