Objective evidence that small-fiber polyneuropathy underlies some illnesses currently labeled as fibromyalgia
- PMID: 23748113
- PMCID: PMC3845002
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.06.001
Objective evidence that small-fiber polyneuropathy underlies some illnesses currently labeled as fibromyalgia
Abstract
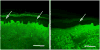
Fibromyalgia is a common, disabling syndrome that includes chronic widespread pain plus diverse additional symptoms. No specific objective abnormalities have been identified, which precludes definitive testing, disease-modifying treatments, and identification of causes. In contrast, small-fiber polyneuropathy (SFPN), despite causing similar symptoms, is definitionally a disease caused by the dysfunction and degeneration of peripheral small-fiber neurons. SFPN has established causes, some diagnosable and definitively treatable, eg, diabetes. To evaluate the hypothesis that some patients labeled as having fibromyalgia have unrecognized SFPN that is causing their illness symptoms, we analyzed SFPN-associated symptoms, neurological examinations, and pathological and physiological markers in 27 patients with fibromyalgia and in 30 matched normal controls. Patients with fibromyalgia had to satisfy the 2010 American College of Rheumatology criteria plus present evidence of a physician's actual diagnosis of fibromyalgia. The study's instruments comprised the Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument (MNSI), the Utah Early Neuropathy Scale (UENS), distal-leg neurodiagnostic skin biopsies, plus autonomic-function testing (AFT). We found that 41% of skin biopsies from subjects with fibromyalgia vs 3% of biopsies from control subjects were diagnostic for SFPN, and MNSI and UENS scores were higher in patients with fibromyalgia than in control subjects (all P ≤ 0.001). Abnormal AFTs were equally prevalent, suggesting that fibromyalgia-associated SFPN is primarily somatic. Blood tests from subjects with fibromyalgia and SFPN-diagnostic skin biopsies provided insights into causes. All glucose tolerance tests were normal, but 8 subjects had dysimmune markers, 2 had hepatitis C serologies, and 1 family had apparent genetic causality. These findings suggest that some patients with chronic pain labeled as fibromyalgia have unrecognized SFPN, a distinct disease that can be tested for objectively and sometimes treated definitively.
Keywords: Autonomic function testing; Chronic pain; Human-subject research; Peripheral nerve; Peripheral neuropathy; Skin biopsy.
Copyright © 2013 International Association for the Study of Pain. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Objective evidence that small-fiber polyneuropathy underlies some illnesses currently labeled as fibromyalgia.Pain. 2013 Nov;154(11):2569. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.06.037. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Pain. 2013. PMID: 23811315 No abstract available.
-
Reply to the letter to the editor.Pain. 2013 Nov;154(11):2569-2571. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.07.016. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Pain. 2013. PMID: 23891683 No abstract available.
References
-
- Assessment: Clinical autonomic testing report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 1996;46:873–880. - PubMed
-
- Aalto AM, Elovainio M, Kivimaki M, Uutela A, Pirkola S. The Beck Depression Inventory and General Health Questionnaire as measures of depression in the general population: a validation study using the Composite International Diagnostic Interview as the gold standard. Psychiatry Res. 2012;197:163–171. - PubMed
-
- Akkaya N, Akkaya S, Atalay NS, Balci CS, Sahin F. Relationship between the body image and level of pain, functional status, severity of depression, and quality of life in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome. Clin Rheumatol. 2012;31:983–988. - PubMed
-
- Amato AA, Oaklander AL. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 16-2004. A 76-year-old woman with pain and numbness in the legs and feet. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2181–2189. - PubMed
-
- Califano D, D’Alessio A, Colucci-D’Amato GL, De Vita G, Monaco C, Santelli G, Di Fiore PP, Vecchio G, Fusco A, Santoro M, de Franciscis V. A potential pathogenetic mechanism for multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 syndromes involves ret-induced impairment of terminal differentiation of neuroepithelial cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 1996;93:7933–7937. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

