Alteration of mitochondrial function and insulin sensitivity in primary mouse skeletal muscle cells isolated from transgenic and knockout mice: role of ogg1
- PMID: 23748360
- PMCID: PMC3713209
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2013-1076
Alteration of mitochondrial function and insulin sensitivity in primary mouse skeletal muscle cells isolated from transgenic and knockout mice: role of ogg1
Abstract
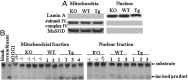
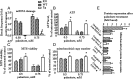
Recent evidence has linked mitochondrial dysfunction and DNA damage, increased oxidative stress in skeletal muscle, and insulin resistance (IR). The purpose of this study was to determine the role of the DNA repair enzyme, human 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase/apurinic/apyrimidinic lyase (hOGG1), on palmitate-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and IR in primary cultures of skeletal muscle derived from hind limb of ogg1(-/-) knockout mice and transgenic mice, which overexpress human (hOGG1) in mitochondria (transgenic [Tg]/MTS-hOGG1). Following exposure to palmitate, we evaluated mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) damage, mitochondrial function, production of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (mtROS), mitochondrial mass, JNK activation, insulin signaling pathways, and glucose uptake. Palmitate-induced mtDNA damage, mtROS, mitochondrial dysfunction, and activation of JNK were all diminished, whereas ATP levels, mitochondrial mass, insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of Akt (Ser 473), and insulin sensitivity were increased in primary myotubes isolated from Tg/MTS-hOGG1 mice compared to myotubes isolated from either knockout or wild-type mice. In addition, both basal and maximal respiratory rates during mitochondrial oxidation on pyruvate showed a variable response, with some animals displaying an increased respiration in muscle fibers isolated from the transgenic mice. Our results support the model that DNA repair enzyme OGG1 plays a pivotal role in repairing mtDNA damage, and consequently, in mtROS production and regulating downstream events leading to IR in skeletal muscle.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Protection from palmitate-induced mitochondrial DNA damage prevents from mitochondrial oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis, and impaired insulin signaling in rat L6 skeletal muscle cells.Endocrinology. 2012 Jan;153(1):92-100. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-1442. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22128025 Free PMC article.
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibition ameliorates palmitate-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in skeletal muscle cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:1435-1446. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.09.019. Epub 2013 Oct 10. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 24120971
-
Mitochondria-targeted Ogg1 and aconitase-2 prevent oxidant-induced mitochondrial DNA damage in alveolar epithelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 28;289(9):6165-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.515130. Epub 2014 Jan 15. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24429287 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of OGG1 in transcriptional regulation and maintenance of metabolic homeostasis.DNA Repair (Amst). 2019 Sep;81:102667. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2019.102667. Epub 2019 Jul 8. DNA Repair (Amst). 2019. PMID: 31311771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Scoping Review Investigating the "Gene-Dosage Theory" of Mitochondrial DNA in the Healthy Skeletal Muscle.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 2;24(9):8154. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098154. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175862 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Plasma mitochondrial DNA is elevated in obese type 2 diabetes mellitus patients and correlates positively with insulin resistance.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 10;14(10):e0222278. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222278. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31600210 Free PMC article.
-
On the epigenetic role of guanosine oxidation.Redox Biol. 2020 Jan;29:101398. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101398. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Redox Biol. 2020. PMID: 31926624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial DNA Repair through OGG1 Activity Attenuates Breast Cancer Progression and Metastasis.Cancer Res. 2016 Jan 1;76(1):30-4. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0692. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26586787 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial OGG1 expression reduces age-associated neuroinflammation by regulating cytosolic mitochondrial DNA.Free Radic Biol Med. 2023 Jul;203:34-44. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.03.262. Epub 2023 Apr 1. Free Radic Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37011700 Free PMC article.
-
8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase (OGG1) deficiency elicits coordinated changes in lipid and mitochondrial metabolism in muscle.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 20;12(7):e0181687. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181687. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28727777 Free PMC article.
References
-
- DeFronzo RA. Lilly lecture 1987. The triumvirate: β-cell, muscle, liver. A collusion responsible for NIDDM. Diabetes. 1988;37:667-687 - PubMed
-
- Yuzefovych LV, Solodushko VA, Wilson GL, Rachek LI. Protection from palmitate-induced mitochondrial DNA damage prevents from mitochondrial oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis, and impaired insulin signaling in rat L6 skeletal muscle cells. Endocrinology. 2012;153:92-100 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

