Quantitative computed tomography in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- PMID: 23748651
- PMCID: PMC4161463
- DOI: 10.1097/RTI.0b013e318298733c
Quantitative computed tomography in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Abstract
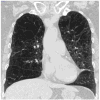
Quantitative computed tomography is being increasingly used to quantify the features of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, specifically emphysema, air trapping, and airway abnormality. For quantification of emphysema, the density mask technique is most widely used, with threshold on the order of-950 HU, but percentile cutoff may be less sensitive to volume changes. Sources of variation include depth of inspiration, scanner make and model, technical parameters, and cigarette smoking. On expiratory computed tomography (CT), air trapping may be quantified by evaluating the percentage of lung volume less than a given threshold (eg, -856 HU) by comparing lung volumes and attenuation on expiration and inspiration or, as done more recently, by coregistering inspiratory and expiratory CT scans. All of these indices correlate well with the severity of physiological airway obstruction. By constructing a 3-dimensional model of the airway from volumetric CT, it is possible to measure dimensions (external and internal diameters and airway wall thickness) of segmental and subsegmental airways orthogonal to their long axes. Measurement of airway parameters correlates with the severity of airflow obstruction and with the history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease exacerbation.
Figures








References
-
- Centers for Disease Control. Deaths: Final Data for 2010. 2013 [cited 2013 Feb 23, 2013]; Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/dvs/deaths_2010_release.pdf. - PubMed
-
- Global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. 2013 [cited 2013]; Available from: http://www.goldcopd.org/uploads/users/files/GOLD_Report_2013_Feb20.pdf.
-
- Gietema HA, Schilham AM, van Ginneken B, van Klaveren RJ, Lammers JW, Prokop M. Monitoring of smoking-induced emphysema with CT in a lung cancer screening setting: detection of real increase in extent of emphysema. Radiology. 2007 Sep;244(3):890–7. - PubMed
-
- Coxson HO, Dirksen A, Edwards LD, Yates JC, Agusti A, Bakke P, et al. The presence and progression of emphysema in COPD as determined by CT scanning and biomarker expression: a prospective analysis from the ECLIPSE study. Lancet Respiratory Medicine. 2013 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

