Characterization of glycoproteins in equine herpesvirus-1
- PMID: 23748975
- PMCID: PMC3942931
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.13-0168
Characterization of glycoproteins in equine herpesvirus-1
Abstract
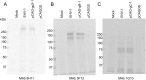
In this study, we attempted to express twelve glycoproteins of equine herpesvirus-1 (EHV-1) in 293T cells and to characterize these using monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) and horse sera against EHV-1. Expression of glycoprotein B (gB), gC, gD, gG, gI and gp2 was recognized by immunoblot analysis using horse sera, but that of gE, gH, gK, gL, gM and gN was not. Four MAbs recognized gB, four recognized gC and one recognized gp2. Two MAbs against gB cross-reacted with EHV-4. Interestingly, coexpression of gE and gI and gM and gN enhanced their antigenicity. Furthermore, immunoblot analysis of gp2 showed that different molecular masses of gp2 were recognized by the MAb against gp2 and horse sera against EHV-1. In this study, it was demonstrated that at least six glycoproteins were immunogenic to horses, and coexpression of gE and gI and gM and gN was important for enhancement of antigenicity.
Figures


References
-
- Allen G. P., Bryans J. T.1986. Molecular epizootiology, pathogenesis, and prophylaxis of equine herpesvirus-1 infections. Prog. Vet. Microbiol. Immunol. 2: 78–144 - PubMed
-
- Allen G. P., Kydd J. H., Slater J. D., Smith K. C.1999. Advances in understanding of the pathogenesis, epidemiology and immunological control of equine herpesvirus abortion. pp. 129–146. In: Equine Infectious Diseases VIII, Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference (Wernery, U., Wade, J. A., Mumford, J. A. and Kaaden, O.R. eds.), R&W Publications, Newmarket.
-
- Andoh K., Takasugi M., Mahmoud H. Y. A., Hattori S., Terada Y., Noguchi K., Shimoda H., Bannai H., Tsujimura K., Matsumura T., Kondo T., Maeda K.2013. Identification of a major immunogenic region of equine herpesvirus-1 glycoprotein E and its application to enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Vet. Microbiol. 164: 18–26. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.01.033 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boussif O., Lezoualc’h F., Zanta M. A., Mergny M. D., Scherman D., Demeneix B., Behr J. P.1995. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92: 7297–7301. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.16.7297 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

