Enhanced inhibition of bladder cancer cell growth by simultaneous knockdown of antiapoptotic Bcl-xL and survivin in combination with chemotherapy
- PMID: 23749114
- PMCID: PMC3709786
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms140612297
Enhanced inhibition of bladder cancer cell growth by simultaneous knockdown of antiapoptotic Bcl-xL and survivin in combination with chemotherapy
Abstract
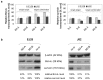
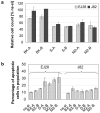
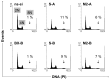
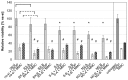
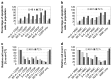
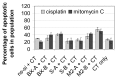
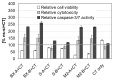
The overexpression of antiapoptotic genes, such as Bcl-xL and survivin, contributes to the increased survival of tumor cells and to the development of treatment resistances. In the bladder cancer cell lines EJ28 and J82, the siRNA-mediated knockdown of survivin reduces cell proliferation and the inhibition of Bcl-xL sensitizes these cells towards subsequent chemotherapy with mitomycin C and cisplatin. Therefore, the aim of this study was to analyze if the simultaneous knockdown of Bcl-xL and survivin might represent a more powerful treatment option for bladder cancer than the single inhibition of one of these target genes. At 96 h after transfection, reduction in cell viability was stronger after simultaneous inhibition of Bcl-xL and survivin (decrease of 40%-48%) in comparison to the single target treatments (decrease of 29% at best). Furthermore, simultaneous knockdown of Bcl-xL and survivin considerably increased the efficacy of subsequent chemotherapy. For example, cellular viability of EJ28 cells decreased to 6% in consequence of Bcl-xL and survivin inhibition plus cisplatin treatment whereas single target siRNA plus chemotherapy treatments mediated reductions down to 15%-36% only. In conclusion, the combination of simultaneous siRNA-mediated knockdown of antiapoptotic Bcl-xL and survivin-a multitarget molecular-based therapy-and conventional chemotherapy shows great potential for improving bladder cancer treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Simultaneous siRNA-mediated knockdown of antiapoptotic BCL2, Bcl-xL, XIAP and survivin in bladder cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2012 Oct;41(4):1271-7. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1549. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22797576 Free PMC article.
-
siRNA-mediated inhibition of antiapoptotic genes enhances chemotherapy efficacy in bladder cancer cells.Anticancer Res. 2012 Oct;32(10):4313-8. Anticancer Res. 2012. PMID: 23060552
-
Antisense- and siRNA-mediated inhibition of the anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-xL for chemosensitization of bladder cancer cells.Int J Oncol. 2015 Sep;47(3):1121-30. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3096. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26201840
-
Multitarget siRNA inhibition of antiapoptotic genes (XIAP, BCL2, BCL-X(L)) in bladder cancer cells.Anticancer Res. 2008 Jul-Aug;28(4B):2259-63. Anticancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18751404
-
The dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BGT226 induces cell cycle arrest and regulates Survivin gene expression in human pancreatic cancer cell lines.Tumour Biol. 2012 Jun;33(3):757-65. doi: 10.1007/s13277-011-0290-2. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Tumour Biol. 2012. PMID: 22170433
Cited by
-
Growth inhibition and chemo-radiosensitization of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by survivin-shRNA lentivirus transfection.Oncol Lett. 2018 Oct;16(4):4813-4820. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9280. Epub 2018 Aug 8. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30250546 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic therapy in urologic cancers: an update on clinical trials.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 14;8(7):12484-12500. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14226. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28036257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenomic and Metabolomic Integration Reveals Dynamic Metabolic Regulation in Bladder Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 31;13(11):2719. doi: 10.3390/cancers13112719. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34072826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of a Novel Integrase-Deficient Lentivirus for Targeted Anti-Cancer Therapy With Survivin Promoter-Driven Diphtheria Toxin A.Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Aug;94(31):e1301. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001301. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 26252309 Free PMC article.
-
Intravesicular administration of sodium hyaluronate ameliorates the inflammation and cell proliferation of cystitis cystica et glandularis involving interleukin-6/JAK2/Stat3 signaling pathway.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 21;7(1):15892. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16088-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29162939 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ferlay J., Parkin D.M., Steliarova-Foucher E. Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2008. Eur. J. Cancer. 2010;46:765–781. - PubMed
-
- Sylvester R.J., Brausi M.A., Kirkels W.J., Hoeltl W., Calais Da Silva F., Powell P.H., Prescott S., Kirkali Z., van de Beek C., Gorlia T., et al. Long-term efficacy results of EORTC genito-urinary group randomized phase 3 study 30911 comparing intravesical instillations of epirubicin, bacillus Calmette-Guerin, and bacillus Calmette-Guerin plus isoniazid in patients with intermediate- and high-risk stage Ta T1 urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Eur. Urol. 2010;57:766–773. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Witjes J.A., Compérat E., Cowan N.C., de Santis M., Gakis G., Lebret T., Ribal M.J., Sherif A. Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer. Uroweb. 2013. [(accessed on 17 April 2013)]. Available online: http://www.uroweb.org/gls/pdf/07_Bladder%20Cancer_LRV2.pdf. - PubMed
-
- Babjuk M., Burger M., Zigeuner R., Shariat S.F., van Rhijn B., Compérat E., Sylvester R.J., Kaasinen E., Böhle A., Palou J., et al. Guidelines on Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer (TaT1 and CIS) Uroweb. 2013. [(accessed on 17 April 2013)]. Available online: http://www.uroweb.org/gls/pdf/05_TaT1_Bladder_Cancer_LR.pdf.
-
- Hanahan D., Weinberg R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

