Validation of EBUS-TBNA-integrated nodal staging in potentially node-positive non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 23749650
- PMCID: PMC3763161
- DOI: 10.1007/s11748-013-0263-z
Validation of EBUS-TBNA-integrated nodal staging in potentially node-positive non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Objective: Nodal staging of lung cancer is important for selecting surgical candidates. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) was evaluated as a modality for nodal staging of patients with potentially node-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
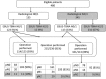
Methods: Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration was used for nodal staging of NSCLC patients with radiological N2/3 disease (short axis >10 mm on computed tomography and/or standardized positron emission uptake value >2.5 on 2-deoxy-2[F-18] fluoro-D-glucose positron emission tomography), T-stage ≥ T2, or positive serum carcinoembryonic antigen. Data on eligible patients were extracted from the database of our institution and analyzed for differences in nodal stages between radiological staging (RS) and EBUS-TBNA-integrated staging (ES), with validation by pathological staging of patients who had undergone surgery.
Results: Of 480 eligible patients, there were 135 N0/1 and 345 N2/3 patients according to RS. Out of the 345 patients staged as N2/3 by RS, 113 (33 %) were downgraded to N0/1 by ES. Out of the 135 patients staged as N0/1 by RS, 12 (9 %) were upgraded to N2/3 by ES. Patients were restaged as N0/1 in 236 cases and N2/3 in 244 cases by ES, and the distributions of nodal stage between RS and ES were significantly different (p < 0.001). Finally, 215 out of the 236 ES-N0/1 patients underwent lung resection, and 195 (90.7 %) and 20 patients were staged by pathology as N0/1 and N2, respectively.
Conclusions: Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration is more accurate for lymph node staging compared to radiological staging. EBUS-TBNA can identify patients who are true candidates for surgery.
Figures
References
-
- Pearson FG, DeLarue NC, Ilves R, Todd TR, Cooper JD. Significance of positive superior mediastinal nodes identified at mediastinoscopy in patients with resectable cancer of the lung. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1982;83:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Gould MK, Kuschner WG, Rydzak CE, Maclean CC, Demas AN, Shigemitsu H, et al. Test performance of positron emission tomography and computed tomography for mediastinal staging in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2003;139:879–892. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-139-11-200311180-00013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Detterbeck FC, Jantz MA, Wallace M, Vansteenkiste J, Silvestri GA; American College of Chest Physicians. Invasive mediastinal staging of lung cancer: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd ed). Chest 2007;132(3 Suppl):202S–20S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

