Restless legs syndrome and daytime sleepiness are prominent in myotonic dystrophy type 2
- PMID: 23749798
- PMCID: PMC3770170
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31829a340f
Restless legs syndrome and daytime sleepiness are prominent in myotonic dystrophy type 2
Abstract
Objectives: Although sleep disturbances are common in myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1), sleep disturbances in myotonic dystrophy type 2 (DM2) have not been well-characterized. We aimed to determine the frequency of sleep disturbances in DM2.
Methods: We conducted a case-control study of 54 genetically confirmed DM2 subjects and 104 medical controls without DM1 or DM2, and surveyed common sleep disturbances, including symptoms of probable restless legs syndrome (RLS), excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), sleep quality, fatigue, obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), probable REM sleep behavior disorder (pRBD), and pain. Thirty patients with DM2 and 43 controls responded to the survey. Group comparisons with parametric statistical tests and multiple linear and logistic regression analyses were conducted for the dependent variables of EDS and poor sleep quality.
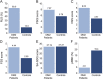
Results: The mean ages of patients with DM2 and controls were 63.8 and 64.5 years, respectively. Significant sleep disturbances in patients with DM2 compared to controls included probable RLS (60.0% vs 14.0%, p < 0.0001), EDS (p < 0.001), sleep quality (p = 0.02), and fatigue (p < 0.0001). EDS and fatigue symptoms were independently associated with DM2 diagnosis (p < 0.01) after controlling for age, sex, RLS, and pain scores. There were no group differences in OSA (p = 0.87) or pRBD (p = 0.12) scores.
Conclusions: RLS, EDS, and fatigue are frequent sleep disturbances in patients with DM2, while OSA and pRBD symptoms are not. EDS was independently associated with DM2 diagnosis, suggesting possible primary CNS hypersomnia mechanisms. Further studies utilizing objective sleep measures are needed to better characterize sleep comorbidities in DM2.
Figures
Comment in
-
Restless legs syndrome and daytime sleepiness are prominent in myotonic dystrophy type 2.Neurology. 2014 Jan 21;82(3):283-4. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000443031.44463.36. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 24446176 No abstract available.
-
Author response: Erik K. St. Louis, Erek M. Lam, Paul W. Shepard, Rochester, MN.Neurology. 2014 Jan 21;82(3):284. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 24592486 No abstract available.
-
Restless legs syndrome and daytime sleepiness are prominent in myotonic dystrophy type 2.Neurology. 2014 Aug 5;83(6):572. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000453225.02417.cf. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 25092929 No abstract available.
-
Author Response.Neurology. 2014 Aug 5;83(6):573. Neurology. 2014. PMID: 25237694 No abstract available.
References
-
- Turner C, Hilton-Jones D. The myotonic dystrophies: diagnosis and management. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2010;81:358–367 - PubMed
-
- Ashizawa T, Sarkar PS. Myotonic dystrophy types 1 and 2. Handb Clin Neurol 2011;101:193–237 - PubMed
-
- Liquori CL, Ricker K, Moseley ML, et al. Myotonic dystrophy type 2 caused by a CCTG expansion in intron 1 of ZNF9. Science 2001;293:864–867 - PubMed
-
- Laberge L, Bégin P, Montplaisir J, et al. Sleep complaints in patients with myotonic dystrophy. J Sleep Res 2004;13:95–100 - PubMed
-
- Laberge L, Bégin P, Dauvilliers Y, et al. A polysomnographic study of daytime sleepiness in myotonic dystrophy type 1. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2009;80:642–646 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
