Dysfunctional cortical connectivity during the auditory oddball task in patients with schizophrenia
- PMID: 23750187
- PMCID: PMC3636485
- DOI: 10.2174/1874440001307010015
Dysfunctional cortical connectivity during the auditory oddball task in patients with schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: We studied the imaginary coherence (IC) of gamma frequency oscillations between brain regions of male schizophrenia patients during an auditory oddball task using magnetoencephalography (MEG) and electroencephalography (EEG).
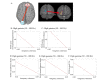
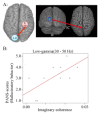
Methods: Subjects were 10 right-handed male schizophrenia patients, evaluated by the positive and negative symptom scale (PANSS), and 10 healthy controls. Functional connectivity during the auditory oddball task was reconstructed in low (30-50 Hz) and high (50-100 Hz) gamma bands, and represented by imaginary coherence (IC) based on significant oscillatory power changes. We calculated correlations between PANSS scores and IC.
Results: In the high gamma band, IC between left occipital and right prefrontal lobe areas during the time window 750-1000 ms from stimulus onset showed negative correlations with total negative scores, total positive scores, the sum of positive and negative scores in PANSS, conceptual disorganization, and social avoidance scores. In the low gamma band, IC between the same areas from 250-500 ms also showed a negative correlation with the conceptual disorganization score. In the same time window, IC between left occipital and right frontoparietal lobe areas in the low gamma band showed a positive correlation with hallucinatory behavior; IC between right temporal pole and left prefrontal lobe areas showed a positive correlation with delusion scores, although these ICs were decreased relative to controls.
Conclusions: Functional disconnection of high and low gamma bands in auditory oddball task may play an important role in the auditory processing in schizophrenia patients.
Keywords: Magnetoencephalography; P300.; PANSS; functional connectivity; gamma band; schizophrenia.
Figures




References
-
- Roth WT, Cannon EH. Some features of the auditory evoked response in schizophrenics. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1972;27:466–71. - PubMed
-
- Roth WT, Pfefferbaum A, Horvath TB, Berger PA, Kopell BS. P3 reduction in auditory evoked potentials of schizophrenics. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1980;49:497–505. - PubMed
-
- Brecher M, Begleiter H. Event-related brain potentials to high-incentive stimuli in unmedicated schizophrenic patients. Biol Psychiatry. 1983;18:661–74. - PubMed
-
- Pfefferbaum A, Wenegrat BG, Ford JM, Roth WT, Kopell BS. Clinical application of the P3 component of event-related potentials. II. Dementia depression and schizophrenia. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1984;59:104–24. - PubMed
-
- Duncan CC. Event-related brain potentials a window on information processing in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1988;14:199–203. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
