Monitoring influenza epidemics in china with search query from baidu
- PMID: 23750192
- PMCID: PMC3667820
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064323
Monitoring influenza epidemics in china with search query from baidu
Abstract
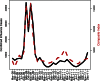
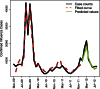
Several approaches have been proposed for near real-time detection and prediction of the spread of influenza. These include search query data for influenza-related terms, which has been explored as a tool for augmenting traditional surveillance methods. In this paper, we present a method that uses Internet search query data from Baidu to model and monitor influenza activity in China. The objectives of the study are to present a comprehensive technique for: (i) keyword selection, (ii) keyword filtering, (iii) index composition and (iv) modeling and detection of influenza activity in China. Sequential time-series for the selected composite keyword index is significantly correlated with Chinese influenza case data. In addition, one-month ahead prediction of influenza cases for the first eight months of 2012 has a mean absolute percent error less than 11%. To our knowledge, this is the first study on the use of search query data from Baidu in conjunction with this approach for estimation of influenza activity in China.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (2009) Influenza (Seasonal), WHO website. Available: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs211/en/, Accessed 11 November 2012.
-
- Vasileios L, Tijl De Bie, Nello C (2010) Flu detector: tracking epidemics on twitter. In Proceedings of the 2010 European conference on Machine learning and knowledge discovery in databases: Part III (ECML PKDD'10), José Luis Balcázar, Francesco Bonchi, Aristides Gionis, and Michèle Sebag (Eds.). Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg: 599–602.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical