The visual system's intrinsic bias and knowledge of size mediate perceived size and location in the dark
- PMID: 23751007
- PMCID: PMC3876294
- DOI: 10.1037/a0033088
The visual system's intrinsic bias and knowledge of size mediate perceived size and location in the dark
Abstract
Dimly lit targets in the dark are perceived as located about an implicit slanted surface that delineates the visual system's intrinsic bias (Ooi, Wu, & He, 2001). If the intrinsic bias reflects the internal model of visual space-as proposed here-its influence should extend beyond target localization. Our first 2 experiments demonstrated that the intrinsic bias also influences perceived target size. We employed a size-matching task and an action task to measure the perceived size of a dimly lit target at various locations in the dark. Then using the size distance invariance hypothesis along with the accurately perceived target angular declination, we converted the perceived sizes to locations. We found that the derived locations from the size judgment tasks can be fitted by slanted curves that resemble the intrinsic bias profile from judged target locations. Our third experiment revealed that armed with the explicit knowledge of target size, an observer perceives target locations in the dark following an intrinsic bias-like profile that is shifted slightly farther from the observer than the profile obtained without knowledge of target size (i.e., slightly more veridical). Altogether, we showed that the intrinsic bias serves as an internal model, or memory, of ground surface layouts when the visual system cannot rely on external depth information. This memory/model can also be weakly influenced by top-down knowledge.
PsycINFO Database Record (c) 2013 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures




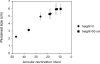




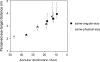
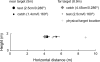
References
-
- Aznar-Casanova JA, Keil SK, Moreno M, Supèr H. Differential intrinsic bias of the 3-D perceptual environment and its role in shape constancy. Experimental Brain Research. 2011;215(1):35–43. - PubMed
-
- Bian Z, Braunstein ML, Andersen GJ. The ground dominance effect in the perception of 3-D layout. Perception & Psychophysics. 2005;67(5):802–815. - PubMed
-
- Bian Z, Braunstein ML, Andersen GJ. The ground dominance effect in the perception of relative distance in 3-D scenes is mainly due to characteristics of the ground surface. Perception & Psychophysics. 2006;68(8):1297–1309. - PubMed
-
- Braunstein ML. Motion and texture as sources of slant information. Journal of Experimental Psychology. 1968;78(2):247–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

