Nutritional status of patients with alcoholic cirrhosis undergoing liver transplantation: time trends and impact on survival
- PMID: 23751180
- PMCID: PMC3987667
- DOI: 10.1111/tri.12123
Nutritional status of patients with alcoholic cirrhosis undergoing liver transplantation: time trends and impact on survival
Abstract
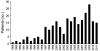
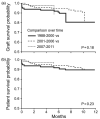
Alcoholic cirrhotics evaluated for liver transplantation are frequently malnourished or obese. We analyzed alcoholic cirrhotics undergoing transplantation to examine time trends of nutrition/weight, transplant outcome, and effects of concomitant hepatitis C virus (HCV) and/or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Nutrition and transplant outcomes were reviewed for alcoholic cirrhosis with/without HCV/HCC. Malnutrition was defined by subjective global assessment. Body mass index (BMI) classified obesity. A total of 261 patients receiving transplants were separated (1988-2000, 2001-2006, and 2007-2011) to generate similar size cohorts. Mean BMI for the whole cohort was 28 ± 6 with 68% classified as overweight/obese. Mean BMI did not vary among cohorts and was not affected by HCV/HCC. While prevalence of malnutrition did not vary among cohorts, it was lower in patients with HCV/HCC (P < 0.01). One-year graft/patient survival was 90% and not impacted by time period, HCV/HCC, or malnutrition after adjusting for demographics and model end-stage liver disease (MELD). Alcoholic cirrhotics undergoing transplantation are malnourished yet frequently overweight/obese. Among patients selected for transplantation, 1-year post-transplant graft/patient survival is excellent, have not changed over time, and do not vary by nutrition/BMI. Our findings support feasibility of liver transplantation for alcoholic cirrhotics with obesity and malnutrition.
Keywords: alcoholic liver disease; hepatitis C virus; hepatocellular carcinoma; malnutrition; mortality; orthotopic liver transplantation.
© 2013 Steunstichting ESOT. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Mendenhall CL, Anderson S, Weesner RE, Goldberg SJ, Crolic KA. Protein-calorie malnutrition associated with alcoholic hepatitis. Veterans Administration Cooperative Study Group on Alcoholic Hepatitis. Am J Med. 1984;76:211. - PubMed
-
- Mullen WH, Churchouse SJ, Vadgama PM. Enzyme electrode for glucose based on the quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase. Analyst. 1985;110:925. - PubMed
-
- Wyatt E. A growing epidemic. ONS Connect. 2010;25:6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

