Reelin, an extracellular matrix protein linked to early onset psychiatric diseases, drives postnatal development of the prefrontal cortex via GluN2B-NMDARs and the mTOR pathway
- PMID: 23752244
- PMCID: PMC3965840
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2013.66
Reelin, an extracellular matrix protein linked to early onset psychiatric diseases, drives postnatal development of the prefrontal cortex via GluN2B-NMDARs and the mTOR pathway
Erratum in
- Mol Psychiatry. 2014 Apr;19(4):527. Gonzalez-Campo, C [added]
Abstract
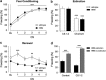
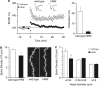
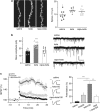
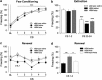
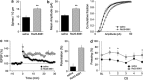
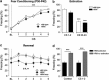
Defective brain extracellular matrix (ECM) is a factor of vulnerability in various psychiatric diseases such as schizophrenia, depression and autism. The glycoprotein reelin is an essential building block of the brain ECM that modulates neuronal development and participates to the functions of adult central synapses. The reelin gene (RELN) is a strong candidate in psychiatric diseases of early onset, but its synaptic and behavioral functions in juvenile brain circuits remain unresolved. Here, we found that in juvenile reelin-haploinsufficient heterozygous reeler mice (HRM), abnormal fear memory erasure is concomitant to reduced dendritic spine density and anomalous long-term potentiation in the prefrontal cortex. In juvenile HRM, a single in vivo injection with ketamine or Ro25-6981 to inhibit GluN2B-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) restored normal spine density, synaptic plasticity and converted fear memory to an erasure-resilient state typical of adult rodents. The functional and behavioral rescue by ketamine was prevented by rapamycin, an inhibitor of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. Finally, we show that fear memory erasure persists until adolescence in HRM and that a single exposure to ketamine during the juvenile period reinstates normal fear memory in adolescent mice. Our results show that reelin is essential for successful structural, functional and behavioral development of juvenile prefrontal circuits and that this developmental period provides a critical window for therapeutic rehabilitation with GluN2B-NMDAR antagonists.
Figures
References
-
- Dityatev A, Schachner M, Sonderegger P. The dual role of the extracellular matrix in synaptic plasticity and homeostasis. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010;11:735–746. - PubMed
-
- Knuesel I. Reelin-mediated signaling in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases. Prog Neurobiol. 2010;91:257–274. - PubMed
-
- D'Arcangelo G, Miao GG, Chen SC, Soares HD, Morgan JI, Curran T. A protein related to extracellular matrix proteins deleted in the mouse mutant reeler. Nature. 1995;374:719–723. - PubMed
-
- Herz J, Y Chen. Reelin lipoprotein receptors and synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:850–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

