Impact of short term consumption of diets high in either non-starch polysaccharides or resistant starch in comparison with moderate weight loss on indices of insulin sensitivity in subjects with metabolic syndrome
- PMID: 23752495
- PMCID: PMC3725498
- DOI: 10.3390/nu5062144
Impact of short term consumption of diets high in either non-starch polysaccharides or resistant starch in comparison with moderate weight loss on indices of insulin sensitivity in subjects with metabolic syndrome
Abstract
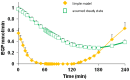
This study investigated if additional non-starch polysaccharide (NSP) or resistant starch (RS), above that currently recommended, leads to better improvement in insulin sensitivity (IS) than observed with modest weight loss (WL). Obese male volunteers (n = 14) were given an energy-maintenance (M) diet containing 27 g NSP and 5 g RS daily for one week. They then received, in a cross-over design, energy-maintenance intakes of either an NSP-enriched diet (42 g NSP, 2.5 g RS) or an RS-enriched diet (16 g NSP, 25 g RS), each for three weeks. Finally, a high protein (30% calories) WL diet was provided at 8 MJ/day for three weeks. During each dietary intervention, endogenous glucose production (EGP) and IS were assessed. Fasting glycaemia was unaltered by diet, but plasma insulin and C-peptide both decreased with the WL diet (p < 0.001), as did EGP (-11%, p = 0.006). Homeostatis model assessment of insulin resistance improved following both WL (p < 0.001) and RS (p < 0.05) diets. Peripheral tissue IS improved only with WL (57%-83%, p < 0.005). Inclusion of additional RS or NSP above amounts currently recommended resulted in little or no improvement in glycaemic control, whereas moderate WL (approximately 3 kg fat) improved IS.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

