Individual and center-level factors affecting mortality among extremely low birth weight infants
- PMID: 23753096
- PMCID: PMC3691533
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2012-3707
Individual and center-level factors affecting mortality among extremely low birth weight infants
Abstract
Objective: To examine factors affecting center differences in mortality for extremely low birth weight (ELBW) infants.
Methods: We analyzed data for 5418 ELBW infants born at 16 Neonatal Research Network centers during 2006-2009. The primary outcomes of early mortality (≤12 hours after birth) and in-hospital mortality were assessed by using multilevel hierarchical models. Models were developed to investigate associations of center rates of selected interventions with mortality while adjusting for patient-level risk factors. These analyses were performed for all gestational ages (GAs) and separately for GAs <25 weeks and ≥25 weeks.
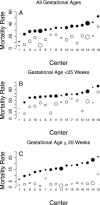
Results: Early and in-hospital mortality rates among centers were 5% to 36% and 11% to 53% for all GAs, 13% to 73% and 28% to 90% for GAs <25 weeks, and 1% to 11% and 7% to 26% for GAs ≥25 weeks, respectively. Center intervention rates significantly predicted both early and in-hospital mortality for infants <25 weeks. For infants ≥25 weeks, intervention rates did not predict mortality. The variance in mortality among centers was significant for all GAs and outcomes. Center use of interventions and patient risk factors explained some but not all of the center variation in mortality rates.
Conclusions: Center intervention rates explain a portion of the center variation in mortality, especially for infants born at <25 weeks' GA. This finding suggests that deaths may be prevented by standardizing care for very early GA infants. However, differences in patient characteristics and center intervention rates do not account for all of the observed variability in mortality; and for infants with GA ≥25 weeks these differences account for only a small part of the variation in mortality.
Keywords: NICU; extremely preterm infants; mortality rates; outcome; preterm infants.
Figures
References
-
- Lee SK, McMillan DD, Ohlsson A, et al. Variations in practice and outcomes in the Canadian NICU network: 1996-1997. Pediatrics. 2000;106(5):1070–1079 - PubMed
-
- Vohr BR, Wright LL, Dusick AM, et al. Neonatal Research Network . Center differences and outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 2004;113(4):781–789 - PubMed
-
- Cotten CM, Oh W, McDonald S, et al. NICHD Neonatal Research Network . Prolonged hospital stay for extremely premature infants: risk factors, center differences, and the impact of mortality on selecting a best-performing center. J Perinatol. 2005;25(10):650–655 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U10 HD021364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40521/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10HD40492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR44/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD53119/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR59/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053124/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD057192/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053119/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD53124/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD34216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR70/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD36790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HD068497/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040521/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053109/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR008084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR125/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001449/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR633/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000442/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD53109/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040461/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40498/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD53089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR7122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR64/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40461/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR39/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR30/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000041/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR007122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR80/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007337/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR8084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR54/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR997/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD053109/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR750/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR32/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD036790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR24139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040498/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

