Contribution of interleukin-12 p35 (IL-12p35) and IL-12p40 to protective immunity and pathology in mice infected with Chlamydia muridarum
- PMID: 23753624
- PMCID: PMC3719579
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00161-13
Contribution of interleukin-12 p35 (IL-12p35) and IL-12p40 to protective immunity and pathology in mice infected with Chlamydia muridarum
Abstract
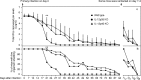
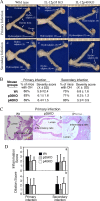
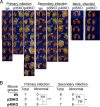
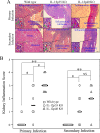
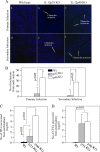
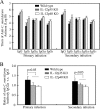
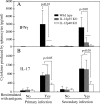
The p35 molecule is unique to interleukin-12 (IL-12), while p40 is shared by both IL-12 and IL-23. IL-12 promotes Th1 T cell responses, while IL-23 promotes Th17 T cell responses. The roles of IL-12p35- and IL-12p40-mediated responses in chlamydial infection were compared in mice following an intravaginal infection with Chlamydia muridarum. Mice deficient in either IL-12p35 or p40 both developed similar but prolonged infection time courses, confirming the roles of IL-12-mediated immune responses in clearing primary infection. However, all mice, regardless of genotype, cleared reinfection within 2 weeks, suggesting that an IL-12- or IL-23-independent adaptive immunity is protective against chlamydial infection. All infected mice developed severe oviduct hydrosalpinx despite the increased Th2 responses in IL-12p35- or IL-12p40-deficient mice, suggesting that Th2-dominant responses can contribute to Chlamydia-induced inflammatory pathology. Compared to IL-12p35 knockout mice, the IL-12p40-deficient mice exhibited more extensive spreading of chlamydial organisms into kidney tissues, leading to significantly increased incidence of pyelonephritis, which both confirms the role of IL-12 or IL-23-independent host responses in Chlamydia-induced pathologies and suggests that in the absence of IL-12/IFN-γ-mediated Th1 immunity, an IL-23-mediated response may play an important role in restricting chlamydial organisms from spreading into distal organs. These observations together provide important information for both understanding chlamydial pathogenesis and developing anti-Chlamydia vaccines.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intranasal vaccination with a secreted chlamydial protein enhances resolution of genital Chlamydia muridarum infection, protects against oviduct pathology, and is highly dependent upon endogenous gamma interferon production.Infect Immun. 2007 Feb;75(2):666-76. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01280-06. Epub 2006 Nov 21. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17118987 Free PMC article.
-
Mice deficient in MyD88 Develop a Th2-dominant response and severe pathology in the upper genital tract following Chlamydia muridarum infection.J Immunol. 2010 Mar 1;184(5):2602-10. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901593. Epub 2010 Feb 1. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20124098
-
Significant role of IL-1 signaling, but limited role of inflammasome activation, in oviduct pathology during Chlamydia muridarum genital infection.J Immunol. 2012 Mar 15;188(6):2866-75. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1103461. Epub 2012 Feb 13. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22331066 Free PMC article.
-
The dual role of cytokine responses to Chlamydia trachomatis infection in host pathogen crosstalk.Microb Pathog. 2022 Dec;173(Pt A):105812. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105812. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Microb Pathog. 2022. PMID: 36209970 Review.
-
Interleukin-35: odd one out or part of the family?Immunol Rev. 2008 Dec;226:248-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00704.x. Immunol Rev. 2008. PMID: 19161429 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lack of long-lasting hydrosalpinx in A/J mice correlates with rapid but transient chlamydial ascension and neutrophil recruitment in the oviduct following intravaginal inoculation with Chlamydia muridarum.Infect Immun. 2014 Jul;82(7):2688-96. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00055-14. Epub 2014 Apr 7. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24711570 Free PMC article.
-
Elimination of Chlamydia muridarum from the female reproductive tract is IL-12p40 dependent, but independent of Th1 and Th2 cells.PLoS Pathog. 2024 Jan 2;20(1):e1011914. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011914. eCollection 2024 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2024. PMID: 38166152 Free PMC article.
-
The role of temporal changes of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the development of adverse cardiac remodeling after ST-elevation myocardial infarction.Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej. 2022 Sep;18(3):217-227. doi: 10.5114/aic.2022.120938. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej. 2022. PMID: 36751290 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling via tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 but not Toll-like receptor 2 contributes significantly to hydrosalpinx development following Chlamydia muridarum infection.Infect Immun. 2014 May;82(5):1833-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01668-13. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24549331 Free PMC article.
-
Murine MicroRNA-214 regulates intracellular adhesion molecule (ICAM1) gene expression in genital Chlamydia muridarum infection.Immunology. 2015 Aug;145(4):534-42. doi: 10.1111/imm.12470. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Immunology. 2015. PMID: 25865776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sherman KJ, Daling JR, Stergachis A, Weiss NS, Foy HM, Wang SP, Grayston JT. 1990. Sexually transmitted diseases and tubal pregnancy. Sex Transm Dis. 17:115–121 - PubMed
-
- Watford WT, Moriguchi M, Morinobu A, O'Shea JJ. 2003. The biology of IL-12: coordinating innate and adaptive immune responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 14:361–368 - PubMed
-
- Hunter CA. 2005. New IL-12-family members: IL-23 and IL-27, cytokines with divergent functions. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5:521–531 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

