The MOV10 helicase inhibits LINE-1 mobility
- PMID: 23754279
- PMCID: PMC3774381
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.465856
The MOV10 helicase inhibits LINE-1 mobility
Abstract
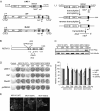
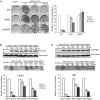
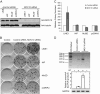
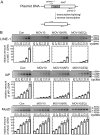
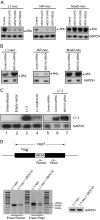
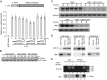
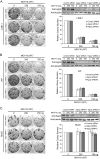
LINE-1 (long interspersed element 1) is an autonomous non-long terminal repeat retrotransposon. Its replication often causes mutation and rearrangement of host genomic DNA. Accordingly, host cells have evolved mechanisms to control LINE-1 mobility. Here, we report that a helicase named MOV10 effectively suppresses LINE-1 transposition. Mutating the helicase motifs impairs this function of MOV10, suggesting that MOV10 requires its helicase activity to suppress LINE-1 replication. Further studies show that MOV10 post-transcriptionally diminishes the level of LINE-1 RNA. The association of MOV10 with both LINE-1 RNA and ORF1 suggests that MOV10 interacts with LINE-1 RNP and consequently causes its RNA degradation. These data demonstrate collectively that MOV10 contributes to the cellular control of LINE-1 replication.
Keywords: Host-Pathogen Interactions; LINE-1; MOV10; Post-transcriptional; RNA Helicase; Restriction; Retrotransposon; Reverse Transcription; Viral Replication; Virology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interplay between RNASEH2 and MOV10 controls LINE-1 retrotransposition.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Feb 28;46(4):1912-1926. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1312. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29315404 Free PMC article.
-
MOV10 Is a 5' to 3' RNA helicase contributing to UPF1 mRNA target degradation by translocation along 3' UTRs.Mol Cell. 2014 May 22;54(4):573-85. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.017. Epub 2014 Apr 10. Mol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24726324
-
The MOV10 helicase restricts hepatitis B virus replication by inhibiting viral reverse transcription.J Biol Chem. 2019 Dec 20;294(51):19804-19813. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009435. Epub 2019 Nov 13. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31722967 Free PMC article.
-
Unwinding the roles of RNA helicase MOV10.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2022 Mar;13(2):e1682. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1682. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2022. PMID: 34327836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of MOV10 in Animal RNA Virus Infection.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Sep 16;7:569737. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.569737. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 33195554 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RNA sensor MDA5 suppresses LINE-1 retrotransposition by regulating the promoter activity of LINE-1 5'-UTR.Mob DNA. 2022 Apr 12;13(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13100-022-00268-0. Mob DNA. 2022. PMID: 35414110 Free PMC article.
-
BST2 Suppresses LINE-1 Retrotransposition by Reducing the Promoter Activity of LINE-1 5' UTR.J Virol. 2022 Jan 26;96(2):e0161021. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01610-21. Epub 2021 Nov 3. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34730388 Free PMC article.
-
Action and function of helicases on RNA G-quadruplexes.Methods. 2022 Aug;204:110-125. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2021.09.003. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Methods. 2022. PMID: 34509630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implications of Endogenous Retroelements in the Etiopathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.J Clin Med. 2021 Feb 19;10(4):856. doi: 10.3390/jcm10040856. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33669709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SAMHD1 Inhibits LINE-1 Retrotransposition by Promoting Stress Granule Formation.PLoS Genet. 2015 Jul 2;11(7):e1005367. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005367. eCollection 2015 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26134849 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belancio V. P., Hedges D. J., Deininger P. (2008) Mammalian non-LTR retrotransposons. For better or worse, in sickness and in health. Genome Res 18, 343–358 - PubMed
-
- Chen J. M., Stenson P. D., Cooper D. N., Férec C. (2005) A systematic analysis of LINE-1 endonuclease-dependent retrotranspositional events causing human genetic disease. Hum. Genet. 117, 411–427 - PubMed
-
- Babushok D. V., Kazazian H. H., Jr. (2007) Progress in understanding the biology of the human mutagen LINE-1. Hum. Mutat. 28, 527–539 - PubMed
-
- Kulpa D. A., Moran J. V. (2006) Cis-preferential LINE-1 reverse transcriptase activity in ribonucleoprotein particles. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 655–660 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

