Childhood obesity prevention and control in city recreation centres and family homes: the MOVE/me Muevo Project
- PMID: 23754782
- PMCID: PMC3785546
- DOI: 10.1111/j.2047-6310.2013.00164.x
Childhood obesity prevention and control in city recreation centres and family homes: the MOVE/me Muevo Project
Abstract
Background: Interventions to prevent and control childhood obesity have shown mixed results in terms of short- and long-term changes.
Objectives: 'MOVE/me Muevo' was a 2-year family- and recreation centre-based randomized controlled trial to promote healthy eating and physical activity among 5- to 8-year-old children. It was hypothesized that children in the intervention group would demonstrate lower post-intervention body mass index (BMI) values and improved obesity-related behaviours compared with the control group children.
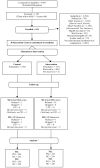
Methods: Thirty recreation centres in San Diego County, California, were randomized to an intervention or control condition. Five hundred forty-one families were enrolled and children's BMI, diet, physical activity and other health indicators were tracked from baseline to 2 years post-baseline. Analyses followed an intent-to-treat approach using mixed-effects models.
Results: No significant intervention effects were observed for the primary outcomes of child's or parent's BMI and child's waist circumference. Moderator analyses, however, showed that girls (but not boys) in the intervention condition reduced their BMI. At the 2-year follow-up, intervention condition parents reported that their children were consuming fewer high-fat foods and sugary beverages.
Conclusions: Favourable implementation fidelity and high retention rates support the feasibility of this intervention in a large metropolitan area; however, interventions of greater intensity may be needed to achieve effects on child's BMI. Also, further research is needed to develop gender-specific intervention strategies so that both genders may benefit from such efforts.
Keywords: Obesity; paediatric; prevention; recreation centres.
© 2013 The Authors. Pediatric Obesity © 2013 International Association for the Study of Obesity.
Figures
References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999-2008. JAMA. 2010;303(3):235–241. - PubMed
-
- Ogden CL, Lamb MM, Carroll MD, Flegal KM. Obesity and socioeconomic status in adults: United States 2005-2008. NCHS Data Brief. 2010;(50):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Reilly JJ, Kelly J. Long-term impact of overweight and obesity in childhood and adolescence on morbidity and premature mortality in adulthood: systematic review. Int J Obesity (London) 2011;35(7):891–898. - PubMed
-
- Hillier F, Pedley C, Summerbell C. Evidence base for primary prevention of obesity in children and adolescents. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2011;54(3):259–264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

