The inevitable journey to being
- PMID: 23754808
- PMCID: PMC3685457
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2012.0254
The inevitable journey to being
Abstract
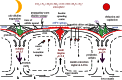
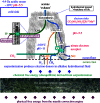
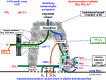
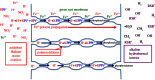
Life is evolutionarily the most complex of the emergent symmetry-breaking, macroscopically organized dynamic structures in the Universe. Members of this cascading series of disequilibria-converting systems, or engines in Cottrell's terminology, become ever more complicated-more chemical and less physical-as each engine extracts, exploits and generates ever lower grades of energy and resources in the service of entropy generation. Each one of these engines emerges spontaneously from order created by a particular mother engine or engines, as the disequilibrated potential daughter is driven beyond a critical point. Exothermic serpentinization of ocean crust is life's mother engine. It drives alkaline hydrothermal convection and thereby the spontaneous production of precipitated submarine hydrothermal mounds. Here, the two chemical disequilibria directly causative in the emergence of life spontaneously arose across the mineral precipitate membranes separating the acidulous, nitrate-bearing CO2-rich, Hadean sea from the alkaline and CH4/H2-rich serpentinization-generated effluents. Essential redox gradients-involving hydrothermal CH4 and H2 as electron donors, CO2 and nitrate, nitrite, and ferric iron from the ambient ocean as acceptors-were imposed which functioned as the original 'carbon-fixing engine'. At the same time, a post-critical-point (milli)voltage pH potential (proton concentration gradient) drove the condensation of orthophosphate to produce a high energy currency: 'the pyrophosphatase engine'.
Keywords: alkaline hydrothermal; carbon fixation; disequilibria; origin of life; pyrophosphatase.
Figures

References
-
- Boltzmann L. 1886. The second law of thermodynamics In Ludwig Boltzmann: theoretical physics and philosophical problems: selected writings (Vienna circle collection) (ed. McGuinness BF.). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Reidel (reprint)
-
- Lane N, Allen JF, Martin W. 2010. How did LUCA make a living? Chemiosmosis in the origin of life. Bioessays 32, 271–280 10.1002/bies.200900131 (doi:10.1002/bies.200900131) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wood BJ, Bryndzia LT, Johnson KE. 1990. Mantle oxidation state and its relation to tectonic environment and fluid speciation. Science 248, 337–345 10.1126/science.248.4953.337 (doi:10.1126/science.248.4953.337) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schrödinger E. 1944. What is life? The physical aspects of the living cell. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press
-
- Harris H. 1999. The birth of the cell. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
