Extralobar pulmonary sequestration
- PMID: 23754900
- PMCID: PMC3658232
- DOI: 10.2147/IMCRJ.S15261
Extralobar pulmonary sequestration
Abstract
Prevalence of pulmonary sequestration accounts for up to 6.4% of all congenital pulmonary malformations. We report on a 40-year-old woman who underwent excision of an aberrant solid retroperitoneal mass in the left subdiaphragmatic area. The mass was identified to be an extralobar pulmonary sequestration. The diagnosis could be made without surgery by percutaneous tissue biopsy and imaging. We encourage keeping in mind pulmonary sequestration anomaly presenting as an aberrant retroperitoneal mass. The aim of this case report is to increase awareness about the condition and review the criteria for its definitive diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: extralobar pulmonary sequestration; retroperitoneal aberrant mass.
Figures
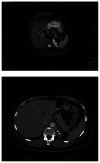
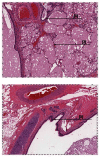
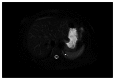
References
-
- Yucel O, Gurkok S, Gozubuyuk A, et al. Diagnosis and surgical treatment of pulmonary sequestration. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2008;56(3):154–157. - PubMed
-
- Salmons S. Pulmonary sequestration. Neonatal Netw. 2000;19(7):27–31. - PubMed
-
- Amitai M, Konen E, Rozenman J, Gerniak A. Preoperative evaluation of pulmonary sequestration by helical CT angiography. Am J Roentgenol. 1996;167(4):1069–1070. - PubMed
-
- Ooi GC, Cheung CW, Lam WK, Tsang KW. Pulmonary sequestration: Diagnosis by magnetic resonance angiography and computed tomography. Chin Med J (Engl) 1999;112(7):668–670. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

