Shigella IpaH0722 E3 ubiquitin ligase effector targets TRAF2 to inhibit PKC-NF-κB activity in invaded epithelial cells
- PMID: 23754945
- PMCID: PMC3675035
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003409
Shigella IpaH0722 E3 ubiquitin ligase effector targets TRAF2 to inhibit PKC-NF-κB activity in invaded epithelial cells
Abstract
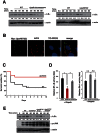
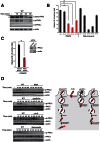
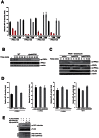
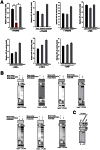
NF-κB plays a central role in modulating innate immune responses to bacterial infections. Therefore, many bacterial pathogens deploy multiple mechanisms to counteract NF-κB activation. The invasion of and subsequent replication of Shigella within epithelial cells is recognized by various pathogen recognition receptors as pathogen-associated molecular patterns. These receptors trigger innate defense mechanisms via the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. Here, we show the inhibition of the NF-κB activation by the delivery of the IpaH E3 ubiquitin ligase family member IpaH0722 using Shigella's type III secretion system. IpaH0722 dampens the acute inflammatory response by preferentially inhibiting the PKC-mediated activation of NF-κB by ubiquitinating TRAF2, a molecule downstream of PKC, and by promoting its proteasome-dependent degradation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Ashida H, Ogawa M, Kim M, Mimuro H, Sasakawa C (2012) Bacteria and host interactions in the gut epithelial barrier. Nat Chem Biol 8: 36–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

