Cellular dissection of the spinal cord motor column by BAC transgenesis and gene trapping in zebrafish
- PMID: 23754985
- PMCID: PMC3664770
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00100
Cellular dissection of the spinal cord motor column by BAC transgenesis and gene trapping in zebrafish
Abstract
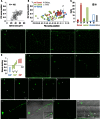
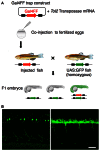
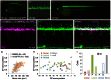
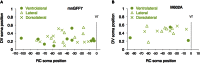
Bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) transgenesis and gene/enhancer trapping are effective approaches for identification of genetically defined neuronal populations in the central nervous system (CNS). Here, we applied these techniques to zebrafish (Danio rerio) in order to obtain insights into the cellular architecture of the axial motor column in vertebrates. First, by using the BAC for the Mnx class homeodomain protein gene mnr2b/mnx2b, we established the mnGFF7 transgenic line expressing the Gal4FF transcriptional activator in a large part of the motor column. Single cell labeling of Gal4FF-expressing cells in the mnGFF7 line enabled a detailed investigation of the morphological characteristics of individual spinal motoneurons, as well as the overall organization of the motor column in a spinal segment. Secondly, from a large-scale gene trap screen, we identified transgenic lines that marked discrete subpopulations of spinal motoneurons with Gal4FF. Molecular characterization of these lines led to the identification of the ADAMTS3 gene, which encodes an evolutionarily conserved ADAMTS family of peptidases and is dynamically expressed in the ventral spinal cord. The transgenic fish established here, along with the identified gene, should facilitate an understanding of the cellular and molecular architecture of the spinal cord motor column and its connection to muscles in vertebrates.
Keywords: ADAMTS3; BAC; Gal4; Mnx; gene trapping; motor column; zebrafish.
Figures



Similar articles
-
An mnr2b/hlxb9lb enhancer trap line that labels spinal and abducens motor neurons in zebrafish.Dev Dyn. 2012 Feb;241(2):327-32. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22781. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Dev Dyn. 2012. PMID: 22128106
-
zTrap: zebrafish gene trap and enhancer trap database.BMC Dev Biol. 2010 Oct 18;10:105. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-10-105. BMC Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20950494 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of BAC transgenic tadpoles enabling live imaging of motoneurons by using the urotensin II-related peptide (ust2b) gene as a driver.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 6;10(2):e0117370. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117370. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25658845 Free PMC article.
-
Gal4 Driver Transgenic Zebrafish: Powerful Tools to Study Developmental Biology, Organogenesis, and Neuroscience.Adv Genet. 2016;95:65-87. doi: 10.1016/bs.adgen.2016.04.002. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Adv Genet. 2016. PMID: 27503354 Review.
-
Energy metabolism in spinal motoneurons of the zebrafish.Eur J Morphol. 1994 Aug;32(2-4):212-6. Eur J Morphol. 1994. PMID: 7803169 Review.
Cited by
-
Spinal cord elongation enables proportional regulation of the zebrafish posterior body.Development. 2025 Jan 1;152(1):dev204438. doi: 10.1242/dev.204438. Epub 2025 Jan 9. Development. 2025. PMID: 39745249 Free PMC article.
-
The Rac-GAP alpha2-Chimaerin Signals via CRMP2 and Stathmins in the Development of the Ocular Motor System.J Neurosci. 2021 Aug 4;41(31):6652-6672. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0983-19.2021. Epub 2021 Jun 24. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34168008 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution analysis of central nervous system expression patterns in zebrafish Gal4 enhancer-trap lines.Dev Dyn. 2015 Jun;244(6):785-96. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24260. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Dev Dyn. 2015. PMID: 25694140 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Live Imaging of Axonal Transport in Developing Zebrafish Axons.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2431:325-350. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1990-2_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35412285
-
Systematic shifts in the balance of excitation and inhibition coordinate the activity of axial motor pools at different speeds of locomotion.J Neurosci. 2014 Oct 15;34(42):14046-54. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0514-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25319701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Appel B., Korzh V., Glasgow E., Thor S., Edlund T., Dawid I. B., et al. (1995). Motoneuron fate specification revealed by patterned LIM homeobox gene expression in embryonic zebrafish. Development 121, 4117–4125 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

