Double-stranded RNA attenuates the barrier function of human pulmonary artery endothelial cells
- PMID: 23755110
- PMCID: PMC3670875
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063776
Double-stranded RNA attenuates the barrier function of human pulmonary artery endothelial cells
Abstract
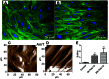
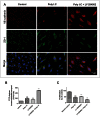
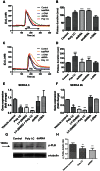
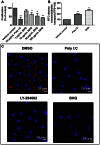
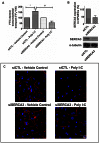
Circulating RNA may result from excessive cell damage or acute viral infection and can interact with vascular endothelial cells. Despite the obvious clinical implications associated with the presence of circulating RNA, its pathological effects on endothelial cells and the governing molecular mechanisms are still not fully elucidated. We analyzed the effects of double stranded RNA on primary human pulmonary artery endothelial cells (hPAECs). The effect of natural and synthetic double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) on hPAECs was investigated using trans-endothelial electric resistance, molecule trafficking, calcium (Ca(2+)) homeostasis, gene expression and proliferation studies. Furthermore, the morphology and mechanical changes of the cells caused by synthetic dsRNA was followed by in-situ atomic force microscopy, by vascular-endothelial cadherin and F-actin staining. Our results indicated that exposure of hPAECs to synthetic dsRNA led to functional deficits. This was reflected by morphological and mechanical changes and an increase in the permeability of the endothelial monolayer. hPAECs treated with synthetic dsRNA accumulated in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Additionally, the proliferation rate of the cells in the presence of synthetic dsRNA was significantly decreased. Furthermore, we found that natural and synthetic dsRNA modulated Ca(2+) signaling in hPAECs by inhibiting the sarco-endoplasmic Ca(2+)-ATPase (SERCA) which is involved in the regulation of the intracellular Ca(2+) homeostasis and thus cell growth. Even upon synthetic dsRNA stimulation silencing of SERCA3 preserved the endothelial monolayer integrity. Our data identify novel mechanisms by which dsRNA can disrupt endothelial barrier function and these may be relevant in inflammatory processes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

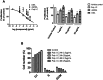
Similar articles
-
Budesonide promotes airway epithelial barrier integrity following double-stranded RNA challenge.PLoS One. 2021 Dec 6;16(12):e0260706. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260706. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34871316 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor-C, a potential paracrine regulator of glomerular permeability, increases glomerular endothelial cell monolayer integrity and intracellular calcium.Am J Pathol. 2008 Oct;173(4):938-48. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070416. Epub 2008 Sep 4. Am J Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18772335 Free PMC article.
-
A role for VEGFR2 activation in endothelial responses caused by barrier disruptive OxPAPC concentrations.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30957. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030957. Epub 2012 Jan 31. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22303475 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Regulation of Vascular Permeability by Vascular Endothelial Cadherin-Mediated Endothelial Cell-Cell Junctions.J Nippon Med Sch. 2017;84(4):148-159. doi: 10.1272/jnms.84.148. J Nippon Med Sch. 2017. PMID: 28978894 Review.
-
The regulation of sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum calcium-ATPases (SERCA).Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015 Oct;93(10):843-54. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2014-0463. Epub 2015 Jan 19. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25730320 Review.
Cited by
-
STIM1/ORAI1-mediated Ca2+ Influx Regulates Enolase-1 Exteriorization.J Biol Chem. 2015 May 8;290(19):11983-99. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.598425. Epub 2015 Mar 24. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25805497 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular RNA as a Versatile DAMP and Alarm Signal That Influences Leukocyte Recruitment in Inflammation and Infection.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Dec 18;8:619221. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.619221. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33392206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activated prostaglandin D2 receptors on macrophages enhance neutrophil recruitment into the lung.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Mar;137(3):833-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.11.012. Epub 2016 Jan 12. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26792210 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Signaling in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension-A Double-Stranded Sword.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 28;21(9):3124. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093124. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32354189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Responses of Endothelial Cells Towards Ischemic Conditioning Following Acute Myocardial Infarction.Cond Med. 2018 Aug;1(5):247-258. Cond Med. 2018. PMID: 30338315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ross R (1999) Mechanisms of disease - atherosclerosis - an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 340: 115–126. - PubMed
-
- Lundberg AM, Drexler SK, Monaco C, Williams LM, Sacre SM, et al. (2007) Key differences in TLR3/poly I : C signaling and cytokine induction by human primary cells: A phenomenon absent from murine cell systems. Blood 110: 3245–3252. - PubMed
-
- Pirher N, Ivicak K, Pohar J, Bencina M, Jerala R (2008) A second binding site for double-stranded RNA in TLR3 and consequences for interferon activation. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 15: 761–763. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

