Lymphoid to myeloid cell trans-differentiation is determined by C/EBPβ structure and post-translational modifications
- PMID: 23755188
- PMCID: PMC3674013
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065169
Lymphoid to myeloid cell trans-differentiation is determined by C/EBPβ structure and post-translational modifications
Abstract
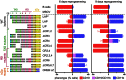
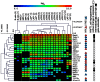
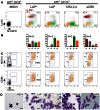
The transcription factor C/EBPβ controls differentiation, proliferation, and functionality of many cell types, including innate immune cells. A detailed molecular understanding of how C/EBPβ directs alternative cell fates remains largely elusive. A multitude of signal-dependent post-translational modifications (PTMs) differentially affect the protean C/EBPβ functions. In this study we apply an assay that converts primary mouse B lymphoid progenitors into myeloid cells in order to answer the question how C/EBPβ regulates (trans-) differentiation and determines myeloid cell fate. We found that structural alterations and various C/EBPβ PTMs determine the outcome of trans-differentiation of lymphoid into myeloid cells, including different types of monocytes/macrophages, dendritic cells, and granulocytes. The ability of C/EBPβ to recruit chromatin remodeling complexes is required for the granulocytic trans-differentiation outcome. These novel findings reveal that PTMs and structural plasticity of C/EBPβ are adaptable modular properties that integrate and rewire epigenetic functions to direct differentiation to diverse innate immune system cells, which are crucial for the organism survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Graf T (2011) Historical origins of transdifferentiation and reprogramming. Cell stem cell 9: 504–516. - PubMed
-
- Laiosa CV, Stadtfeld M, Graf T (2006) Determinants of lymphoid-myeloid lineage diversification. Annual review of immunology 24: 705–738. - PubMed
-
- Tsukada J, Yoshida Y, Kominato Y, Auron PE (2011) The CCAAT/enhancer (C/EBP) family of basic-leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors is a multifaceted highly-regulated system for gene regulation. Cytokine 54: 6–19. - PubMed
-
- Bussmann LH, Schubert A, Vu Manh TP, De Andres L, Desbordes SC, et al. (2009) A robust and highly efficient immune cell reprogramming system. Cell stem cell 5: 554–566. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

