Outpatient therapeutic feeding program outcomes and determinants in treatment of severe acute malnutrition in tigray, northern ethiopia: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 23755286
- PMCID: PMC3675046
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065840
Outpatient therapeutic feeding program outcomes and determinants in treatment of severe acute malnutrition in tigray, northern ethiopia: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Outpatient Therapeutic feeding Program (OTP) brings the services for management of Severe Acute Malnutrition (SAM) closer to the community by making services available at decentralized treatment points within the primary health care settings, through the use of ready-to-use therapeutic foods, community outreach and mobilization. Little is known about the program outcomes. This study revealed the levels of program outcome indictors and determinant factors to recovery rate.
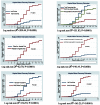
Methods: A retrospective cohort study was conducted on 628 children who had been managed for SAM under OTP from April/2008 to January/2012. The children were selected using systematic random sampling from 12 health posts and 4 health centers. The study relied on information of demographic characteristics, anthropometries, Plumpy'Nut, medical problems and routine medications intakes. The results were estimated using Kaplan-Meier survival curves, log-rank test and Cox-regression.
Results: The recovery, defaulter, mortality and weight gain rates were 61.78%, 13.85%, 3.02% and 5.23 gm/kg/day, respectively. Routine medications were administered partially and children with medical problems were managed inappropriately under the program. As a child consumed one more sachet of Plumpy'Nut, the recovery rate from SAM increased by 4% (HR = 1.04, 95%-CI = 1.03, 1.05, P<0.001). The adjusted hazard ratios to recovery of children with diarrhea, appetite loss with Plumpy'Nut and failure to gain weight were 2.20 (HR = 2.20, 95%-CI = 1.31, 3.41, P = 0.001), 4.49 (HR = 1.74, 95%-CI = 1.07, 2.83, P = 0.046) and 3.88 (HR = 1.95, 95%-CI = 1.17, 3.23, P<0.001), respectively. Children who took amoxicillin and de-worming had 95% (HR = 1.95, 95%-CI = 1.17, 3.23) and 74% (HR = 1.74, 95%-CI = 1.07, 2.83) more probability to recover from SAM as compared to those who didn't take them.
Conclusions: The OTP was partially successful. Management of children with comorbidities under the program and partial administration of routine drugs were major threats for the program effectiveness. The stakeholders should focus on creating the capacity of the OTP providers on proper management of SAM to achieve fully effective program.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- WHO, UNICEF, WFP (2007) Community-based management of severe acute malnutrition. Geneva, Switzerland
-
- Esubalew D, Kiflu M, Tessema T (January 2009) Community Based Emergency Response To Reduce Acute Malnutrition And Improved Access To Nutritional Support And Care. Jarcoo consulting
-
- Chamois S (2011) Decentralization and scale up of outpatient management of SAM in Ethiopia (2008–2010). Filed article 2011: 39–40.
-
- Central Statistical Agency [Ethiopia] and ICF International (2012) Ethiopia Demographic and Health Survey 2011. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia and Calverton, Maryland, USA: Central Statistical Agency and ICF International.
-
- Del R, Joy M (2008) Madagascar's Pilot Program for Community Management of Acute Malnutrition: Evaluation Highlights. Arlington, Va.USA
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

