Signal integration in TGF-β, WNT, and Hippo pathways
- PMID: 23755364
- PMCID: PMC3672943
- DOI: 10.12703/P5-17
Signal integration in TGF-β, WNT, and Hippo pathways
Abstract
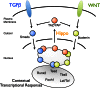
Complete sequences of animal genomes have revealed a remarkably small and conserved toolbox of signalling pathways, such as TGF-β and WNT that account for all biological diversity. This raises the question as to how such a limited set of cues elaborates so many diverse cell fates and behaviours. It is now clear that components of signalling pathways are physically assembled into higher order networks that ultimately dictate the biological output of pathway activity. Intertwining of pathways is thus emerging as a key feature of a large, integrated and coordinated signalling network that allows cells to read a limited set of extrinsic cues, but mount the diverse responses that underpin successful development and homeostasis. Moreover, this design principle confounds the development of effective therapeutic interventions in complex diseases, such as cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Anzano MA, Roberts AB, Meyers CA, Komoriya A, Lamb LC, Smith JM, Sporn MB. Synergistic interaction of two classes of transforming growth factors from murine sarcoma cells. Cancer Res. 1982;42:4776–8. - PubMed
-
- Massague J. Type beta transforming growth factor from feline sarcoma virus-transformed rat cells. Isolation and biological properties. J Biol Chem. 1984;259:9756–61. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

