The role of CARMA1 in T cells
- PMID: 23756245
- PMCID: PMC3690520
- DOI: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.2013007056
The role of CARMA1 in T cells
Abstract
Caspase recruitment domain-containing membrane-associated guanylate kinase protein-1 (CARMA1), a member of the membrane associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) family of kinases, is essential for T lymphocyte activation and proliferation via T-cell receptor (TCR) mediated NF-κB activation. Recent studies suggest a broader role for CARMA1 regulating other T-cell functions as well as a role in non-TCR-mediated signaling pathways important for lymphocyte development and functions. In addition, CARMA1 has been shown to be an important component in the pathogenesis of several human diseases. Thus, comprehensively defining its mechanisms of action and regulation could reveal novel therapeutic targets for T-cell-mediated diseases and lymphoproliferative disorders.
Figures
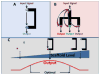
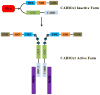
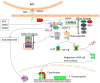
References
-
- Kalia V, Sarkar S, Ahmed R. Fine-tuning CD4+ central memory T cell heterogeneity by strength of stimulation. Eur J Immunol. 2008 Jan;38(1):15–9. - PubMed
-
- Teixeiro E, Daniels MA, Hamilton SE, Schrum AG, Bragado R, Jameson SC, Palmer E. Different T cell receptor signals determine CD8+ memory versus effector development. Science. 2009 Jan 23;323(5913):502–5. - PubMed
-
- Teitell MA, Pandolfi PP. Molecular genetics of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Annu Rev Pathol. 2009;4:175–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

