The structural basis of R-spondin recognition by LGR5 and RNF43
- PMID: 23756651
- PMCID: PMC3701190
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.219915.113
The structural basis of R-spondin recognition by LGR5 and RNF43
Abstract
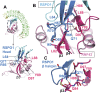
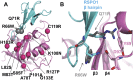
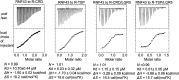
R-spondins (RSPOs) enhance Wnt signaling, affect stem cell behavior, bind to leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptors 4-6, (LGR4-6) and the transmembrane E3 ubiquitin ligases RING finger 43/zinc and RING finger 3 (RNF43/ZNRF3). The structure of RSPO1 bound to both LGR5 and RNF43 ectodomains confirms their physical linkage. RSPO1 is sandwiched by LGR5 and RNF43, with its rod module of the cysteine-rich domain (CRD) contacting LGR5 and a hairpin inserted into RNF43. LGR5 does not contact RNF43 but increases the affinity of RSPO1 to RNF43, supporting LGR5 as an engagement receptor and RNF43 as an effector receptor. Disease mutations map to the RSPO1-RNF43 interface, which promises therapeutic targeting.
Keywords: E3 ubiquitin ligase; LGR5; R-spondin; RNF43; Wnt signaling; furin-like repeat.
Figures


References
-
- Barker N, Clevers H 2010. Leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptors as markers of adult stem cells. Gastroenterology 138: 1681–1696 - PubMed
-
- Barker N, Rookmaaker MB, Kujala P, Ng A, Leushacke M, Snippert H, van de Wetering M, Tan S, Van Es JH, Huch M et al. 2012. Lgr5+ve stem/progenitor cells contribute to nephron formation during kidney development. Cell Rep 2: 540–552 - PubMed
-
- Blaydon DC, Ishii Y, O'Toole EA, Unsworth HC, Teh MT, Ruschendorf F, Sinclair C, Hopsu-Havu VK, Tidman N, Moss C, et al. 2006. The gene encoding R-spondin 4 (RSPO4), a secreted protein implicated in Wnt signaling, is mutated in inherited anonychia. Nat Genet 38: 1245–1247 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
