Agonist activated PKCβII translocation and modulation of cardiac myocyte contractile function
- PMID: 23756828
- PMCID: PMC3679501
- DOI: 10.1038/srep01971
Agonist activated PKCβII translocation and modulation of cardiac myocyte contractile function
Abstract
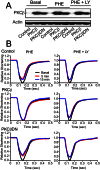
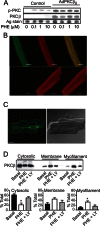
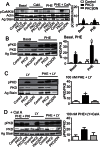
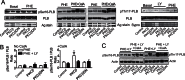
Elevated protein kinase C βII (PKCβII) expression develops during heart failure and yet the role of this isoform in modulating contractile function remains controversial. The present study examines the impact of agonist-induced PKCβII activation on contractile function in adult cardiac myocytes. Diminished contractile function develops in response to low dose phenylephrine (PHE, 100 nM) in controls, while function is preserved in response to PHE in PKCβII-expressing myocytes. PHE also caused PKCβII translocation and a punctate distribution pattern in myocytes expressing this isoform. The preserved contractile function and translocation responses to PHE are blocked by the inhibitor, LY379196 (30 nM) in PKCβII-expressing myocytes. Further analysis showed downstream protein kinase D (PKD) phosphorylation and phosphatase activation are associated with the LY379196-sensitive contractile response. PHE also triggered a complex pattern of end-target phosphorylation in PKCβII-expressing myocytes. These patterns are consistent with bifurcated activation of downstream signaling activity by PKCβII.
Figures




References
-
- Bowling N., Walsh R. A., Song G. J., Estridge T., Sandusky G. E., Fouts R. L., Mintze K., Pickard T., Roden R., Bristow M. R., Sabbah H. N., Mizrahi J. L., Gromo G., King G. L. & Vlahos C. J. Increased protein kinase C activity and expression of Ca2+-sensitive isoforms in the failing human heart. Circulation 99, 384–391 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Takeishi Y., Chu G. X., Kirkpatrick D. M., Li Z. L., Wakasaki H., Kranias E. G., King G. L. & Walsh R. A. In vivo phosphorylation of cardiac troponin I by protein kinase C β2 decreases cardiomyocyte calcium responsiveness and contractility in transgenic mouse hearts. J Clin Invest 102, 72–78 (1998). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gu X. & Bishop S. P. Increased Protein-Kinase-C and Isozyme Redistribution in Pressure-Overload Cardiac-Hypertrophy in the Rat. Circ Res 75, 926–931 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Hambleton M., Hahn H., Pleger S. T., Kuhn M. C., Klevitsky R., Carr A. N., Kimball T. F., Hewett T. E., Dorn G. W. 2nd, Koch W. J. & Molkentin J. D. Pharmacological- and gene therapy-based inhibition of protein kinase Calpha/beta enhances cardiac contractility and attenuates heart failure. Circulation 114, 574–582 (2006). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

