CD25 and CD69 induction by α4β1 outside-in signalling requires TCR early signalling complex proteins
- PMID: 23758320
- PMCID: PMC3749870
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20130485
CD25 and CD69 induction by α4β1 outside-in signalling requires TCR early signalling complex proteins
Abstract
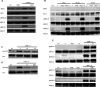
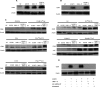
Distinct signalling pathways producing diverse cellular outcomes can utilize similar subsets of proteins. For example, proteins from the TCR (T-cell receptor) ESC (early signalling complex) are also involved in interferon-α receptor signalling. Defining the mechanism for how these proteins function within a given pathway is important in understanding the integration and communication of signalling networks with one another. We investigated the contributions of the TCR ESC proteins Lck (lymphocyte-specific kinase), ZAP-70 (ζ-chain-associated protein of 70 kDa), Vav1, SLP-76 [SH2 (Src homology 2)-domain-containing leukocyte protein of 76 kDa] and LAT (linker for activation of T-cells) to integrin outside-in signalling in human T-cells. Lck, ZAP-70, SLP-76, Vav1 and LAT were activated by α4β1 outside-in signalling, but in a manner different from TCR signalling. TCR stimulation recruits ESC proteins to activate the mitogen-activated protein kinase ERK (extracellular-signal-regulated kinase). α4β1 outside-in-mediated ERK activation did not require TCR ESC proteins. However, α4β1 outside-in signalling induced CD25 and co-stimulated CD69 and this was dependent on TCR ESC proteins. TCR and α4β1 outside-in signalling are integrated through the common use of TCR ESC proteins; however, these proteins display functionally distinct roles in these pathways. These novel insights into the cross-talk between integrin outside-in and TCR signalling pathways are highly relevant to the development of therapeutic strategies to overcome disease associated with T-cell deregulation.
Figures








References
-
- Petricoin E. F., Ito S., Williams B. L., Audet S., Stancato L. F., Gamero A., Clouse K., Grimley P., Weiss A., Beeler J., et al. Antiproliferative action of interferon-α requires components of T-cell-receptor signaling. Nature. 1997;390:629–632. - PubMed
-
- Micouin A., Wietzerbin J., Steunou V., Martyré M. C. p95(vav) associates with type I interferon (IFN) receptor and contributes to the antiproliferative effect of IFN-α in megakaryocytic cell lines. Oncogene. 2000;19:387–394. - PubMed
-
- Ticchioni M., Charvet C., Noraz N., Lamy L., Steinberg M., Bernard A., Deckert M. Signaling through ZAP-70 is required for CXCL12-mediated T-cell transendothelial migration. Blood. 2002;99:3111–3118. - PubMed
-
- Kremer K. N., Humphreys T. D., Kumar A., Qian N. X., Hedin K. E. Distinct role of ZAP-70 and Src homology 2 domain-containing leukocyte protein of 76 kDa in the prolonged activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase by the stromal cell-derived factor-1 α/CXCL12 chemokine. J. Immunol. 2003;171:360–367. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed Z., Beeton C. A., Williams M. A., Clements D., Baldari C. T., Ladbury J. E. Distinct spatial and temporal distribution of ZAP70 and Lck following stimulation of interferon and T-cell receptors. J. Mol. Biol. 2005;353:1001–1010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

