Gene panel model predictive of outcome in patients with prostate cancer
- PMID: 23758475
- PMCID: PMC3727569
- DOI: 10.1089/omi.2012.0124
Gene panel model predictive of outcome in patients with prostate cancer
Abstract
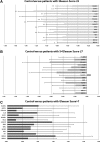
In men at high risk for prostate cancer, established clinical and pathological parameters provide only limited prognostic information. Here we analyzed a French cohort of 103 prostate cancer patients and developed a gene panel model predictive of outcome in this group of patients. The model comprised of a 15-gene TaqMan Low-Density Array (TLDA) card, with gene expressions compared to a standardized reference. The RQ value for each gene was calculated, and a scoring system was developed. Summing all the binary scores (0 or 1) corresponding to the 15 genes, a global score is obtained between 0 and 15. This global score can be compared to Gleason score (0 to 10) by recalculating it into a 0-10 scaled score. A scaled score ≥2 suggested that the patient is suffering from a prostate cancer, and a scaled score ≥7 flagged aggressive cancer. Statistical analyses demonstrated a strongly significant linear correlation (p=3.50E-08) between scaled score and Gleason score for this prostate cancer cohort (N=103). These results support the capacity of this designed 15 target gene TLDA card approach to predict outcome in prostate cancer, opening up a new avenue for personalized medicine through future independent replication and applications for rapid identification of aggressive prostate cancer phenotypes for early intervention.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlation of a Commercial Genomic Risk Classifier with Histological Patterns in Prostate Cancer.J Urol. 2019 Jul;202(1):90-95. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000175. Epub 2019 Jun 7. J Urol. 2019. PMID: 30810466
-
Immunohistochemical expression of Ets-related gene-transcriptional factor in adenocarcinoma prostate and its correlation with Gleason score.Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2016 Oct-Dec;59(4):489-495. doi: 10.4103/0377-4929.191794. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27721279
-
Use of two gene panels for prostate cancer diagnosis and patient risk stratification.Tumour Biol. 2016 Aug;37(8):10115-22. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4619-0. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26820133
-
Radiomics Features Measured with Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Predict Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness.J Urol. 2019 Sep;202(3):498-505. doi: 10.1097/JU.0000000000000272. Epub 2019 Aug 8. J Urol. 2019. PMID: 30958743
-
A 17-Gene Genomic Prostate Score Assay Provides Independent Information on Adverse Pathology in the Setting of Combined Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Fusion Targeted and Systematic Prostate Biopsy.J Urol. 2018 Sep;200(3):564-572. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 Mar 7. J Urol. 2018. PMID: 29524506
Cited by
-
The association between histone 3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) and prostate cancer: relationship with clinicopathological parameters.BMC Cancer. 2014 Dec 23;14:994. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-994. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25535400 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Gene Expression Profiling for Prostate Cancer Risk Assessment: A Systematic Review.Biomed Hub. 2017 May 17;2(2):1-15. doi: 10.1159/000472146. eCollection 2017 May-Aug. Biomed Hub. 2017. PMID: 31988908 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adjakly M. Bosviel R. Rabiau N, et al. DNA methylation and soy phytoestrogens: Quantitative study in DU-145 and PC-3 human prostate cancer cell lines. Epigenomics. 2011;3:795–803. - PubMed
-
- Blute ML. Bergstralh EJ. Iocca A. Scherer B. Zincke H. Use of Gleason score, prostate specific antigen, seminal vesicle and margin status to predict biochemical failure after radical prostatectomy. J Urol. 2001;165:119–125. - PubMed
-
- Brawley OW. Prostate cancer epidemiology in the United States. World J Urol. 2012;30:195–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

