Changes in the micromorphology of the corneal subbasal nerve plexus in patients after plaque brachytherapy
- PMID: 23759072
- PMCID: PMC3691838
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-8-136
Changes in the micromorphology of the corneal subbasal nerve plexus in patients after plaque brachytherapy
Abstract
Background: To quantify the development of radiation neuropathy in corneal subbasal nerve plexus (SNP) after plaque brachytherapy, and the subsequent regeneration of SNP micromorphology and corneal sensation.
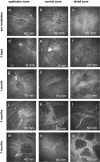
Methods: Nine eyes of 9 melanoma patients (ciliary body: 3, iris: 2, conjunctiva: 4) underwent brachytherapy (ruthenium-106 plaque, dose to tumour base: 523 ± 231 Gy). SNP micromorphology was assessed by in-vivo confocal microscopy. Using software developed in-house, pre-irradiation findings were compared with those obtained after 3 days, 1, 4 and 7 months, and related to radiation dose and corneal sensation.
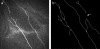
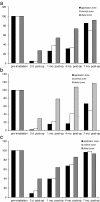
Results: After 3 days nerve fibres were absent from the applicator zone and central cornea, and corneal sensation was abolished. The earliest regenerating fibres were seen at the one-month follow-up. By 4 months SNP structures had increased to one-third of pre-treatment status (based on nerve fibre density and nerve fibre count), and corneal sensation had returned to approximately two-thirds of pre-irradiation values. Regeneration of SNP and corneal sensation was nearly complete 7 months after plaque brachytherapy.
Conclusions: The evaluation of SNP micromorphology and corneal sensation is a reliable and clinically useful method for assessing neuropathy after plaque brachytherapy. Radiation-induced neuropathy of corneal nerves develops quickly and is partly reversible within 7 months. The clinical impact of radiation-induced SNP damage is moderate.
Figures

References
-
- Char DH, Quivey JM, Castro JR, Kroll S, Phillips T. Helium ions versus iodine 125 brachytherapy in the management of uveal melanoma. A prospective, randomized, dynamically balanced trial. Ophthalmology. 1993;100:1547–1554. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

