Application of monoclonal antibody G250 recognizing carbonic anhydrase IX in renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 23759990
- PMCID: PMC3709739
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms140611402
Application of monoclonal antibody G250 recognizing carbonic anhydrase IX in renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
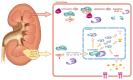
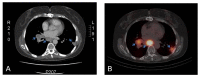
Monoclonal antibody G250 (mAbG250) recognizes a determinant on carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX). CAIX is expressed by virtually all renal cell carcinomas of the clear cell type (ccRCC), but expression in normal tissues is restricted. The homogeneous CAIX expression in ccRCC and excellent targeting capability of mAbG250 in animal models led to the initiation of the clinical evaluation of mAbG250 in (metastatic) RCC (mRCC) patients. Clinical studies confirmed the outstanding targeting ability of mAbG250 and cG250 PET imaging, as diagnostic modality holds great promise for the future, both in detecting localized and advanced disease. Confirmation of the results obtained in the non-randomized clinical trials with unmodified cG250 is needed to substantiate the value of cG250 treatment in mRCC. cG250-Based radio immuno-therapy (RIT) holds promise for treatment of patients with small-volume disease, and adjuvant treatment with unmodified cG250 may be of value in selected cases. In the upcoming years, ongoing clinical trials should provide evidence for these assumptions. Lastly, whether cG250-based RIT can be combined with tyrosine kinase inhibitors, which constitutes the current standard treatment for mRCC, needs to be established.
Figures

References
-
- Jemal A., Siegel R., Ward E., Hao Y., Xu J., Thun M.J. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2009;59:225–249. - PubMed
-
- Patard J.J., Pignot G., Escudier B., Eisen T., Bex A., Sternberg C., Rini B., Roigas J., Choueiri T., Bukowski R., et al. Icud-eau international consultation on kidney cancer 2010: Treatment of metastatic disease. Eur. Urol. 2011;60:684–690. - PubMed
-
- Motzer R.J., Rini B.I., Bukowski R.M., Curti B.D., George D.J., Hudes G.R., Redman B.G., Margolin K.A., Merchan J.R., Wilding G., et al. Sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. JAMA. 2006;295:2516–2524. - PubMed
-
- Escudier B., Eisen T., Stadler W.M., Szczylik C., Oudard S., Siebels M., Negrier S., Chevreau C., Solska E., Desai A.A., et al. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007;356:125–134. - PubMed
-
- Rixe O., Bukowski R.M., Michaelson M.D., Wilding G., Hudes G.R., Bolte O., Motzer R.J., Bycott P., Liau K.F., Freddo J., et al. Axitinib treatment in patients with cytokine-refractory metastatic renal-cell cancer: A phase II study. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:975–984. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

