Effects of long-term oral administration of arachidonic acid and docosahexaenoic acid on the immune functions of young rats
- PMID: 23760060
- PMCID: PMC3725485
- DOI: 10.3390/nu5061949
Effects of long-term oral administration of arachidonic acid and docosahexaenoic acid on the immune functions of young rats
Abstract
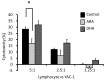
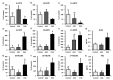
Natural killer (NK) cells have many functional activities, including cytotoxicity and the capacity to produce cytokines and chemokines. NK cell activity is regulated partly by eicosanoids, which are produced from arachidonic acid (ARA) and eicosapentaenoic (EPA) acid. In this study, we investigated the effects of long-term therapy with ARA or docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) on the cytotoxic effects of the NK cells of young rats, which were fed on a nonfish oil diet for two generations. Control oil, ARA (240 mg/kg BW/day) or DHA (240 mg/kg BW/day) were orally administrated to the rats for 13 weeks before determining the cytotoxic activity of NK cells from the spleen against YAC-1 mouse lymphoma cell line, as well as the plasma levels of docosanoids or eicosanoids and inflammatory cytokines. Long-term ARA administration significantly suppressed the cytotoxic activity of NK cells. Moreover, ARA administration significantly increased the plasma levels of ARA, prostaglandin (PG) E2, and PGD2. However, DHA administration did not produce any different effects compared with those in the control rats. Furthermore, the inflammatory cytokine levels were not affected by the administration of ARA or DHA. These results suggest that long-term ARA administration has an inhibitory effect on the tumor cytotoxicity of NK cells in rat spleen lymphocytes owing to the enhanced synthesis of PGE2 and PGD2 from ARA because of the elevated plasma ARA levels in young rats.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Chronic Arachidonic Acid Administration Decreases Docosahexaenoic Acid- and Eicosapentaenoic Acid-Derived Metabolites in Kidneys of Aged Rats.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 20;10(10):e0140884. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140884. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26485038 Free PMC article.
-
Eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids alter rat spleen leukocyte fatty acid composition and prostaglandin E2 production but have different effects on lymphocyte functions and cell-mediated immunity.Lipids. 1998 Feb;33(2):171-80. doi: 10.1007/s11745-998-0193-y. Lipids. 1998. PMID: 9507239
-
Low levels of eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids mimic the effects of fish oil upon rat lymphocytes.Life Sci. 1998;62(24):2209-17. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(98)00199-4. Life Sci. 1998. PMID: 9627080
-
Intake of arachidonic acid-containing lipids in adult humans: dietary surveys and clinical trials.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Apr 16;18(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1039-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 30992005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arachidonic acid needed in infant formula when docosahexaenoic acid is present.Nutr Rev. 2016 May;74(5):329-36. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuw007. Epub 2016 Mar 24. Nutr Rev. 2016. PMID: 27013482 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential effects of docoosahexaenoic and arachidonic acid on fatty acid composition and myosin heavy chain-related genes of slow- and fast-twitch skeletal muscle tissues.Mol Cell Biochem. 2016 Apr;415(1-2):169-81. doi: 10.1007/s11010-016-2689-y. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Mol Cell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27021216
-
Influence of Ovophospholipids on Lymphocyte Subsets and Humoral Immune Response in Mice.Molecules. 2025 May 22;30(11):2253. doi: 10.3390/molecules30112253. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40509141 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Arachidonic Acid Administration Decreases Docosahexaenoic Acid- and Eicosapentaenoic Acid-Derived Metabolites in Kidneys of Aged Rats.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 20;10(10):e0140884. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140884. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26485038 Free PMC article.
-
Omega-3 fatty acids protect renal functions by increasing docosahexaenoic acid-derived metabolite levels in SHR.Cg-Lepr(cp)/NDmcr rats, a metabolic syndrome model.Molecules. 2014 Mar 17;19(3):3247-63. doi: 10.3390/molecules19033247. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 24642910 Free PMC article.
-
Oxylipin secretion by human CD3+ T lymphocytes in vitro is modified by the exogenous essential fatty acid ratio and life stage.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 14;14:1206733. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1206733. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37388745 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

