Colour-encoded paramagnetic microbead-based direct inhibition triplex flow cytometric immunoassay for ochratoxin A, fumonisins and zearalenone in cereals and cereal-based feed
- PMID: 23760139
- PMCID: PMC3765849
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-013-7095-7
Colour-encoded paramagnetic microbead-based direct inhibition triplex flow cytometric immunoassay for ochratoxin A, fumonisins and zearalenone in cereals and cereal-based feed
Abstract
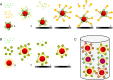
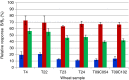
A combined (triplex) immunoassay for the simultaneous detection of three mycotoxins in grains was developed with superparamagnetic colour-encoded microbeads, in combination with two bead-dedicated flow cytometers. Monoclonal antibodies were coupled to the beads, and the amounts of bound mycotoxins were inversely related to the amounts of bound fluorescent labelled mycotoxins (inhibition immunoassay format). The selected monoclonal antibodies were tested for their target mycotoxins and for cross-reactivity with relevant metabolites and masked mycotoxins. In the triplex format, low levels of cross-interactions between the assays occurred at irrelevant high levels only. All three assays were influenced by the sample matrix of cereal extracts to some extent, and matrix-matched calibrations are recommended for quantitative screening purposes. In a preliminary in-house validation, the triplex assay was found to be reproducible, sensitive and sufficiently accurate for the quantitative screening at ML level. The triplex assay was critically compared to liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry using reference materials and fortified blank material. Results for the quantification of ochratoxin A and zearalenone were in good agreement. However, the fumonisin assay was, due to overestimation, only suitable for qualitative judgements. Both flow cytometer platforms (Luminex 100 and FLEXMAP 3D) performed similar with respect to sensitivity with the advantages of a higher sample throughput and response range of the FLEXMAP 3D and lower cost of the Luminex 100.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Validation of the 11+Myco MS-PREP® Method for Determination of Aflatoxins, Fumonisins, Deoxynivalenol, Ochratoxin A, Zearalenone, HT-2, and T-2 Toxins in Cereals, Baby Food, Spices, and Animal Feed by Immunoaffinity Column with LC-MS/MS: AOAC Performance Tested MethodSM 112401.J AOAC Int. 2025 Mar 1;108(2):207-252. doi: 10.1093/jaoacint/qsae097. J AOAC Int. 2025. PMID: 39661480 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous determination of deoxynivalenol, zearalenone, T-2-toxin and some masked metabolites in different cereals and cereal-derived food.Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2012;29(5):819-35. doi: 10.1080/19440049.2012.656707. Epub 2012 Feb 27. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2012. PMID: 22369426
-
Co-occurrence of aflatoxins, ochratoxin A, fumonisins, and zearalenone in cereals and feed, determined by competitive direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and thin-layer chromatography.Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2009 Dec;60(4):427-34. doi: 10.2478/10004-1254-60-2009-1975. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2009. PMID: 20061243
-
Emerging nanotechnology for detection of mycotoxins in food and feed.Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2015;66(4):363-70. doi: 10.3109/09637486.2015.1034251. Epub 2015 May 22. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26001087 Review.
-
Mycotoxins transmitted into beer from contaminated grains during brewing.J AOAC Int. 1996 Jul-Aug;79(4):875-82. J AOAC Int. 1996. PMID: 8757446 Review.
Cited by
-
A flow-cytometry-based method for detecting simultaneously five allergens in a complex food matrix.J Food Sci Technol. 2016 Dec;53(12):4179-4186. doi: 10.1007/s13197-016-2402-x. Epub 2016 Dec 2. J Food Sci Technol. 2016. PMID: 28115758 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Current Methods for Analysis of Mycotoxins in Herbal Medicines.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Feb 2;10(2):65. doi: 10.3390/toxins10020065. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29393905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abundance of HPV L1 Intra-Genotype Variants With Capsid Epitopic Modifications Found Within Low- and High-Grade Pap Smears With Potential Implications for Vaccinology.Front Genet. 2019 May 24;10:489. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00489. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31231420 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an Ultrasensitive and Rapid Fluorescence Polarization Immunoassay for Ochratoxin A in Rice.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Oct 29;12(11):682. doi: 10.3390/toxins12110682. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33138019 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Simple and Rapid Bead-Based Cytometric Immunoassays Using Superparamagnetic Hybrid Core-Shell Microparticles.ACS Meas Sci Au. 2024 Sep 17;4(6):678-688. doi: 10.1021/acsmeasuresciau.4c00038. eCollection 2024 Dec 18. ACS Meas Sci Au. 2024. PMID: 39713030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rodrigues I, Naehrer K. Biomin Survey 2010: mycotoxins inseparable from animal commodities and feed. AllAboutFeed. 2011;2(2):17–20.
-
- Pedrosa K, Borutova R. Synergistic effects of mycotoxins discussed. Feedstuffs. 2011;83(19):1–3.
-
- Jackson LS, Hlywka JJ, Senthil KR, Bullerman LB, Musser SM. Effects of time, temperature, and pH on the stability of fumonisin B1 in an aqueous model system. J Agric Food Chem. 1996;44(3):906–912. doi: 10.1021/jf950364o. - DOI
-
- Shetty PH, Bhat RV. Natural occurrence of fumonisin B1 and its co-occurrence with aflatoxin B1 in Indian sorghum, maize, and poultry feeds. J Agric Food Chem. 1997;45(6):2170–2173. doi: 10.1021/jf960607s. - DOI
-
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs (2006) J Eur Union L364:5–24
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

