Influenza activity--United States, 2012-13 season and composition of the 2013-14 influenza vaccine
- PMID: 23760189
- PMCID: PMC4604847
Influenza activity--United States, 2012-13 season and composition of the 2013-14 influenza vaccine
Abstract
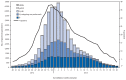
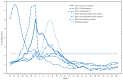
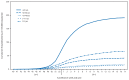
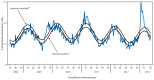
During the 2012-13 influenza season in the United States, influenza activity* increased through November and December before peaking in late December. Influenza A (H3N2) viruses predominated overall, but influenza B viruses and, to a lesser extent, influenza A (H1N1)pdm09 (pH1N1) viruses also were reported in the United States. This influenza season was moderately severe, with a higher percentage of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI), higher rates of hospitalization, and more reported deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza compared with recent years. This report summarizes influenza activity in the United States during the 2012-13 influenza season (September 30, 2012-May 18, 2013) as of June 7, 2013, and reports the recommendations for the components of the 2013-14 Northern Hemisphere influenza vaccine.
Figures
References
-
- Food and Drug Administration. Influenza virus vaccine for the 2013–2014 season. Silver Spring, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration; 2013. Available at http://www.fda.gov/biologicsbloodvaccines/guidancecomplianceregulatoryin....
-
- Gao HN, Lu HZ, Cao B, et al. Clinical findings in 111 cases of influenza A(H7N9) infection. N Engl J Med. 2013 May 22; [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
-
- CDC. Influenza A (H3N2) variant virus-related hospitalizations—Ohio, 2012. MMWR. 2012;61:764–7. - PubMed
-
- CDC. Prevention and control of influenza with vaccines: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) MMWR. 2010;59(RR-8) - PubMed
-
- CDC. Influenza prevention: information for travelers. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2012. Available at http://www.cdc.gov/flu/travelers/travelersfacts.htm.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

