Time series regression studies in environmental epidemiology
- PMID: 23760528
- PMCID: PMC3780998
- DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyt092
Time series regression studies in environmental epidemiology
Abstract
Time series regression studies have been widely used in environmental epidemiology, notably in investigating the short-term associations between exposures such as air pollution, weather variables or pollen, and health outcomes such as mortality, myocardial infarction or disease-specific hospital admissions. Typically, for both exposure and outcome, data are available at regular time intervals (e.g. daily pollution levels and daily mortality counts) and the aim is to explore short-term associations between them. In this article, we describe the general features of time series data, and we outline the analysis process, beginning with descriptive analysis, then focusing on issues in time series regression that differ from other regression methods: modelling short-term fluctuations in the presence of seasonal and long-term patterns, dealing with time varying confounding factors and modelling delayed ('lagged') associations between exposure and outcome. We finish with advice on model checking and sensitivity analysis, and some common extensions to the basic model.
Keywords: Time series; air pollution; environmental epidemiology.
Figures


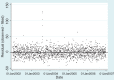
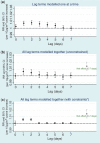
References
-
- Jimenez E, Linares C, Martinez D, Diaz J. Role of Saharan dust in the relationship between particulate matter and short-term daily mortality among the elderly in Madrid (Spain) Sci Total Environ. 2010;408:5729–36. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong B. Models for the relationship between ambient temperature and daily mortality. Epidemiology. 2006;17:624–31. - PubMed
-
- Bell ML, Samet JM, Dominici F. Time-series studies of particulate matter. Annu Rev Public Health. 2004;25:247–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

